|
Even in 1990, NOSS allowed any user to browse a hierarchical directory (showing contact info, job titles, manager/reporting relationships etc), email or instant message anyone, and look at their calendar to see what they When Microsoft Exchange first came out, email was handled with the Exchange client and calendaring was from Schedule+, which had been updated to support Exchange (and lives on in some backward Microsoft lingo, where people who start every sentence with “So,” ask you to send them an S+, meaning, invite them to a meeting). Outlook came along in 1996 and became the preferred and unified way to do email, calendars, address books etc.
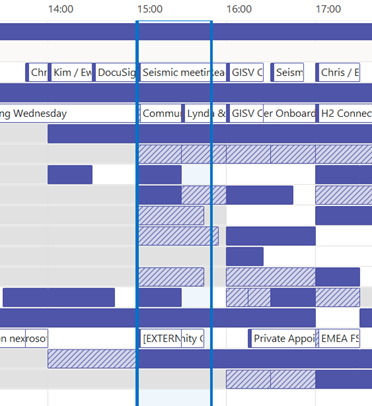
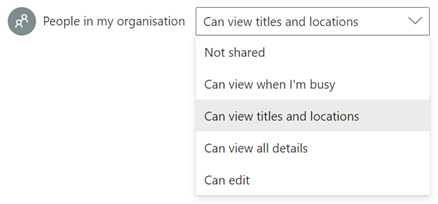
With M365 in general, newly-created mailboxes have no calendar sharing set up, and the action is on the user to choose how to let co-workers see their info. Be a nice person, and check to make sure your colleagues can view your calendar. Ideally, share so that others will see the title and location of any appointment; useful when someone is trying to arrange a meeting, as within the schedule view they can figure out if you are likely to be able to make the proposed meeting time – if your diary is full of blocks marked busy or tentative, they’ll have no idea if you really are in a meeting or have just marked time to do something that you might be happy to move. Or had a colleague’s FYI notice of being on holiday obliterate the view of your calendar. In the early days of Exchange/Outlook, if you had read access to someone’s calendar, you could open up appointments, see who else was attending a meeting, download any attachments and so on, unless the appointment was marked “Private” – though it’s somewhat possible to open Private appointments programmatically if you know what you are doing.
If you choose titles & locations, viewers can’t open your appointments to peer inside, so can’t see who else is attending or what the body of the meeting says, but they can at least see if you’re likely to need travel time between meetings. See here for more info on calendar sharing & delegate access. |
Tag: Outlook
621 – Working Time Directive
|
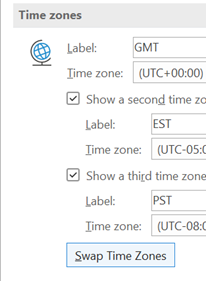
There are whole genres of mechanical watches which can display multiple time zones (check out GMT or World Time if horology is your thing), or you could rely on phone or computer-based aides-memoire, such as displaying multiple time zones alongside your calendar in Outlook, using the Windows Clock app with its world clock view, or even showing several clocks on the Windows task bar.
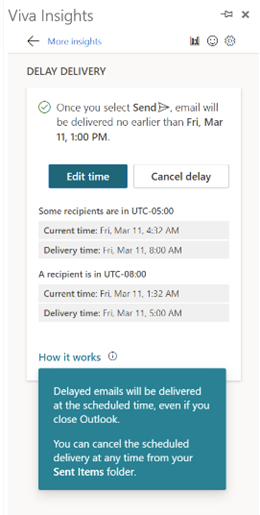
If you have multiple time zones displayed in Outlook, you can switch between them from the settings page – just right-click on the timeline to the side of the calendar and choose Change Time Zone, or go to File | Options | Calendar and look for the settings in there. When you swap them around inside Outlook, it will change the time zone on your PC. In some parts of the world, there’s pressure to prevent “work” from creeping into personal time, meaning emails and other messages should be held back and not If you’re using the right kind of Microsoft 365 subscription, Outlook can offer to delay emails you’re sending to people who are in different time zones – part of the Viva Insights package. Choosing this action has a similar effect to the Delay Delivery The Viva-powered delay option holds the message on the server until the allotted hour, and then delivers it to the recipients – handy if the sender is already outside their working hours by that point… |
612 – New Year, New You (someday/maybe)
|
If we can’t reduce volume of professional communications (be that emails, Teams messages, whatever – just look at Steve cleaning his mailbox and removing >100,000 Sent Items from a single year), then maybe we could do a better job of managing the stuff that we have to deal with. Much ink has been spilled on how to be more effective and how to get things done, but one useful time/focus management principle to revisit is sometimes known as Eisenhower’s Matrix, of which a variety of depictions exist:
The premise is that any task has separate degrees of importance and urgency; we tend to prioritize urgent and overdue things versus things that are actually important. Discipline in task management can give us the clarity to not worry about seemingly urgent yet non-important tasks, and to stay focussed on things which are important, regardless of their urgency. Carve out 75 minutes if you can – because this stuff is important – to watch Randy Pausch’s lecture on Time Management, with the context that when it was recorded, he knew he only had weeks left to live: talk about prioritizing important vs urgent. How you put time and focus management into practice will differ depending on your own style and what tools you want to use. For the Windows / Microsoft 365 user, there are a few quick wins to consider:
|
611 – Finding Ghost meetings
|
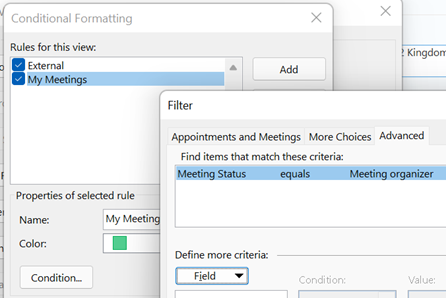
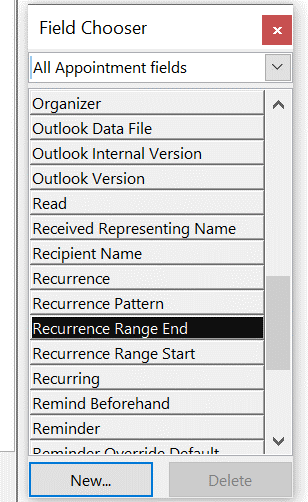
Thinking of meetings you have organised, you can do a few things to make them stand out, like configuring your calendar view to show your own meetings in a different colour. … click Conditional Formatting, add a new rule and click Condition… to set it up. Go to the Advanced tab, click on Field and choose All Appointment Fields, then Meeting Status, then set equals Meeting organizer as the condition, set your colour, font etc choice and save it all out.
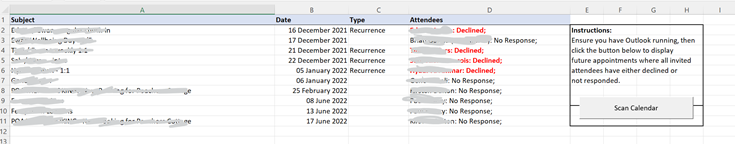
Ghost meetings – you’re organiser, nobody else shows up How many times have you joined an online meeting that you organised, waited a few minutes and then realised that the other party/parties have actually declined but you didn’t notice? Sure, you can see in the tracking tab of a meeting, but might not check until you’ve already started the meeting and wonder why you’re on your Jack Jones. At this time of year, it’s quite likely you’ll have regular meetings with colleagues, customers or partners, and that instance has been declined by all of the invited attendees: the only real solution is to look ahead at your calendar, check the tracking responses and delete meetings which nobody else will attend. What a palaver. Never fear, dear reader. Here’s an Excel spreadsheet with a macro which will list all the future meetings where you are the organiser and all of the attendees have either not responded or have declined, so you can easily decide which ones to go and remove. Download the ZIP file from the link above, save/open it on your PC and you’ll see there’s a single XLSM file within. Open that in Excel, allow changes and enable Macros so it will run, then click the Scan Calendar button to show you a list of meetings that you might be able to delete since everyone else has already bailed out. It will take a couple of minutes to run but will eventually show you a list sorted with the earliest at the top. Have a great holiday season, everyone. See you in the New Year! |
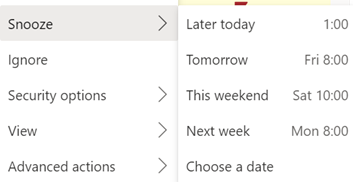
605 – Snooze la differénce
|
One modern incarnation of the multiple-ways principle is electronic mail; despite many attempts to replace email with other means of messaging, persistent chat etc, it’s still a huge deal (especially in business) and it’s still growing. In the days when companies ran their own IT on-premises, there was Exchange, and the companion mail client Outlook arrived shortly after. Web-based consumer services like Hotmail, Yahoo! and Gmail changed the expectations of many users. Home and work email services have been getting closer in form and function since. Microsoft’s current email clients are quite diverged: you can use the full-fat Outlook application to connect to your business email as well as your private The Mail app is pretty good – it can connect to a variety of sources including Office 365, so while it might not be an ideal primary business email application, it can be a good way of connecting to multiple personal email services.
Well, that’s how it works on some combinations. In the browser versions of both Hotmail / Outlook.com and Outlook client and Office 365 – there is no snooze feature. Sorry. Just be more organised. If you snooze an email from another client, it will disappear from Inbox, but when it reappears, it’ll be in the same place as it was before – eg. if you Snooze a 9am email from the web app until 1pm, it will move into the Scheduled folder – but when it moves back into the Inbox, the Outlook and Windows Mail clients will show it down at 9am again so you might as well flag it and be done.
Mobile Outlook and Web clients on Outlook.com or Office 365– Mail disappears and shows up again at the allotted time, right at the top of the mailbox. In the web clients, you’ll see the time stamp of the message as if it has literally just arrived; in the mobile version, though the message is ordered correctly (eg a 9am snooze to reappear at 1pm will show up between 12:30 and 1:15 mails), the displayed time is correct but a little clock icon is shown alongside. Clever. At some point, there is a plan to deliver a single, unified, email client. An Ignite 2020 session talked about the roadmap and further commentary speculated that the One Outlook client may be coming, but isn’t going to be with us for some time yet.
|
599 – Time for a short survey?
|
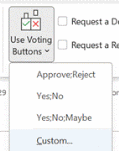
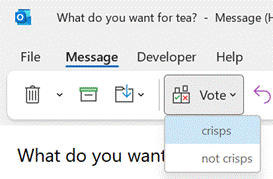
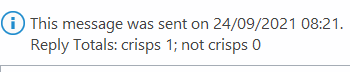
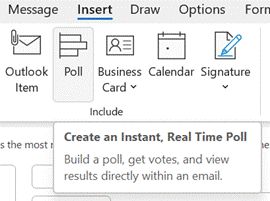
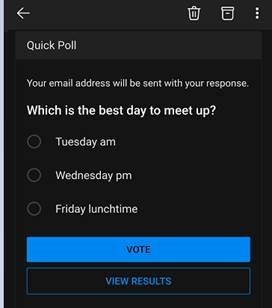
Recipients get prompted in Outlook and can vote with a single click, rather than having to type a response, and the sender can see a Tracking One downside of voting buttons, though, is that they only work in Outlook – there’s no Web App or mobile support, so it does restrict the usability somewhat. Great news, though – a more modern approach is available; not only does it work using the Outlook mobile apps and the browser but it’s a bit more in-your-face for most Outlook users too, with a simple and quick way of responding.
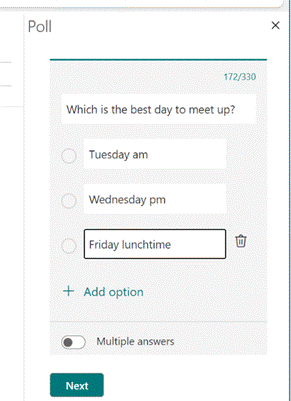
Clicking on the icon gives you a single question with two or more options; it’s powered by Microsoft Forms, but there’s no fancy branching or data validation – it’s a straight “choose one of these short text responses” feature and all the better for it.
Since it’s delivered as part of a Microsoft 365 / Office 365 subscription, it’s a little less slick when dealing with users outside of the organization / tenant (the inline previews don’t show up, so outsiders will need to click the link and use the web UI, and will need to type their email address into the response too), so think of it as a friendly and visible way of collecting simple internal votes. |
594 – One day, meetings != Teams
|
When you create an appointment in Outlook and decide to turn it into a Teams meeting by clicking the icon on the Then there’s the text that gets added to the end of any existing appointment text, which gives dial-in info and provides a link for users who like to click on URLs or who are running a calendaring client which doesn’t support Teams natively. Some degree of customization can be done to this auto-text, but it’s an admin task rather than an end-user one.
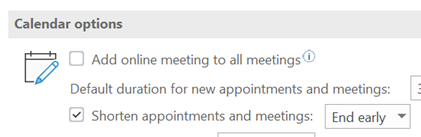
The option is accessed from the main Outlook window, under File | Options | Calendar, and is just above the groovy feature which lets you choose to shorten the default meeting time, so as to allow you and the attendees to get out of your chair once or twice in a working day. From the ToW history files: When you create a thing in your calendar that’s just for you, that’s an Appointment. When you start to invite other people to your thing, then it becomes a Meeting. The Outlook UI changes when you’re dealing with Meetings vs Appointments (e.g., see tracking information on who accepted your meeting invitation, etc). When the Teams integration to Outlook was first rolled out, the workflow to create a meeting was typically to put the time in your diary, invite your desired attendees, then click the Teams Meeting button to add all the extra stuff that anoints the meeting to become a Teams one. That was a one-way process, though – if you clicked in error or decided to forego the online element, you either had to hack out the properties and text (since merely removing the “join” links in the text didn’t get rid of the Join Meeting UI in Outlook, as that was lit up by the contents of the various custom fields in the item) or, more likely, ditch the meeting and create a new one.
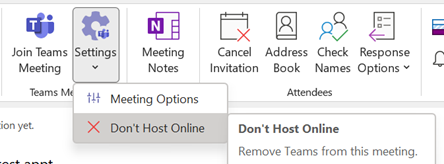
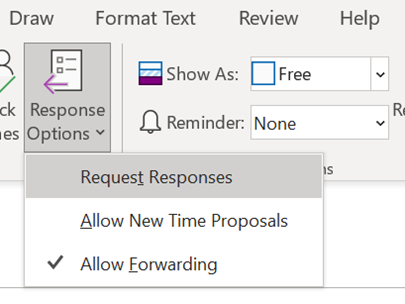
The bypass feature is meeting-specific, so if you are scheduling 1:1s with customers or partners, you might want to let the striaght through, but if hosting a larger meeting then having a lobby could let you get your internal team straight before bringing in your guests. |
579 – Archive that email
|
There are tools – some mythical and magical – to reduce volumes of unnecessary emails, and automatic processing via features like the Focused Inbox or Clutter can help to filter out stuff that is getting in the way, but fundamentally the decision on whether to delete, defer, delegate or just leave it lying about, rests with the user. There is still an AutoArchive function in Outlook, but you probably don’t want to use that.
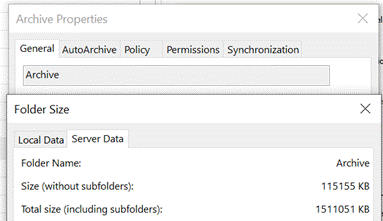
If the Archive option shows up in the web UI (with suitable icon), the folder should also be visible in desktop Outlook in the main folder tree. Just like you have an Inbox, Drafts, Sent Items Check out the Archive folder properties, and you can see its size on your own machine or on the server (assuming that you’re not storing everything in your mailbox within your Outlook cache). To fire an email into the Archive folder from the desktop Outlook client, just press backspace if you’re currently viewing the message in the preview window. The default shortcut key to archive a message in Outlook Web App is E though you can reconfigure the app to use different shortcut schemes, in case you’re more familiar with other web clients. To see the shortcuts in Outlook web app at any time, just press the ? key. |
575 – Who’s meeting?
 Organising a meeting in Outlook means sending out requests to participate – effectively you’re creating an appointment or event in your own calendar, then converting into a meeting by inviting other people to join you. If you’re putting something in your diary and want other people to know about it, but without expecting them to join you (eg you’re going on vacation and presumably don’t want your teammates to tag along), simple tricks can reduce the annoyance you might foist onto your co-workers… Organising a meeting in Outlook means sending out requests to participate – effectively you’re creating an appointment or event in your own calendar, then converting into a meeting by inviting other people to join you. If you’re putting something in your diary and want other people to know about it, but without expecting them to join you (eg you’re going on vacation and presumably don’t want your teammates to tag along), simple tricks can reduce the annoyance you might foist onto your co-workers…
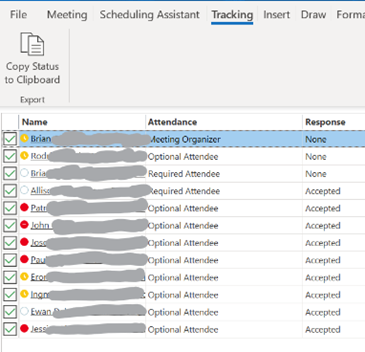
Who has responded? Have most people declined?
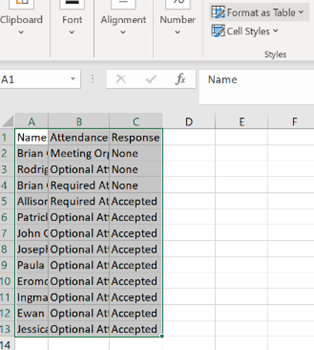
If you are organising or attending a large business meeting with lots of attendees, it’s useful to be able to slice and dice the attendees more effectively – have most people declined and should I move the date, for example – click on the big Copy Status option at the top of the list.
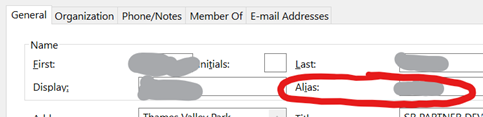
If you right-click the table and select Table > Totals Row then if you filter the headings – like the responses, for example, you’ll be able to quickly see how many Accepted, Declined and so on. What could be interesting, too, is showing attendees names alongside their role, department, which office they’re from, their actual email address etc… Well, thanks to the magic of macros, use this Address Book Resolver spreadsheet, and just paste the responses from the Copy Status… step into cell A1, then hit the Resolve button. Some attendees might be external users (so won’t be known to your address book), and some of the names in the first column might not be unique enough to resolve, and will be highlighted (alongside external users) by a red Unknown in the Job Title column.
To use this sheet for resolving any list of bulk display names or alias names, just paste them into column A (and hide Columns B and C if you’re not using the output from a meeting invite tracking list). To prepare the spreadsheet for use, download the Address Book Resolver file as above (here it is again). Open the ZIP file and open the enclosed XLSM file or save it somewhere on your machine, then open it. Make sure you Enable Editing, then Enable Content so you can run the Macro that does the lookups. This is an evolution of the Alias resolver sheet posted back in ToW 417. |
573 – Searching in Outlook
|
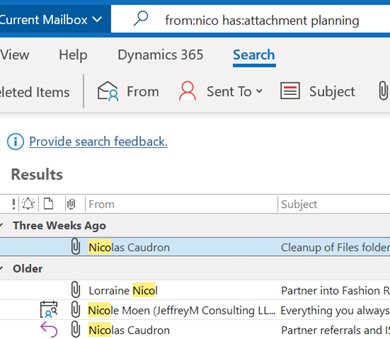
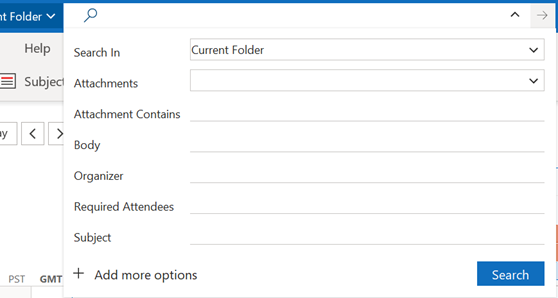
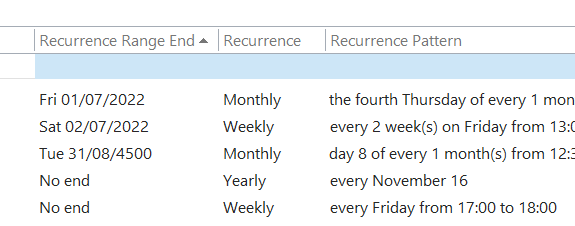
Or has:attachment, which will only show you mails that have other files attached. Combined with a few other criteria, you can filter the results of your search pretty hard, rather than sifting through them. Adding some other smarts like received:”last month” can streamline some more. For more info on search terms, see here. The scenarios our reader posed, though, were specifically around searching in the calendar – eg, do I have a meeting in my calendar with a particular person? Or what recurring appointments are due to expire this month? If you navigate to your Calendar and click the down-pointing arrow to the right of the Search box, it will display a Click + Add more options to bring up a picker that lets you add even more – such as whether the meeting is a recurring one, or if it shows in calendar as Busy or not. Selecting the options builds the query as before, so you can see a variety of defined names – like organizer | organiser (depending on your locale) or requiredattendee:. Coming back to the original question; if you want to find all future meetings in your calendar with anyone called Tony, you could type something like requiredattendee:tony start:>today. And if you want to find out which
Don’t be alarmed if some of them are due to keep happening until a very long way into the future. We’ll probably have stopped using email by then. History Lesson Before Outlook arrived as part of Office 97, users of Exchange Server had an email client and a separate calendar app (Schedule+; that’s why some diehards still say things like “send me an S+”, meaning send a meeting request). Both would maintain a connection to the server and would chat back and forth, only downloading data when a message or attachment was opened. Although this put something of a penalty on the network, it meant there was no need to cache large amounts of data on a PC hard disk. Outlook replaced both the mail and S+ clients, but maintained the same synchronous connection to the server. Outlook 2003 and Exchange 2003 changed the default model, since PC hard disks were getting much bigger and cheaper, so it made sense to have Outlook deal primarily with a cached copy of the user’s mailbox, bringing all kinds of performance benefits to both end user and to the operators of the server back-end. One really notable improvement was the ability to run fast searches against mailbox data that’s in the cache, rather than having to execute searches on the server. Prior to the cached mode, the best-case scenario for running a search was the server returned messages that fit a particular query asked by the client – mails received this week, mails with FOO in the subject line etc. If the server had indexed the relevant properties (received date, subject etc), it was pretty quick at sending back the results. If the user wanted something more in-depth, it was a punishingly slow process as each message would need to be picked up and inspected to see if it met the query – so searching for every email with a particular word in the message body text would be laborious. Three cheers for cached mode and client-side indexing.
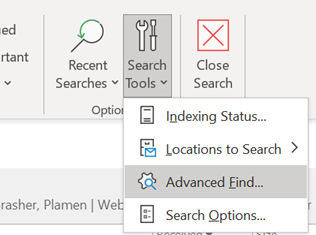
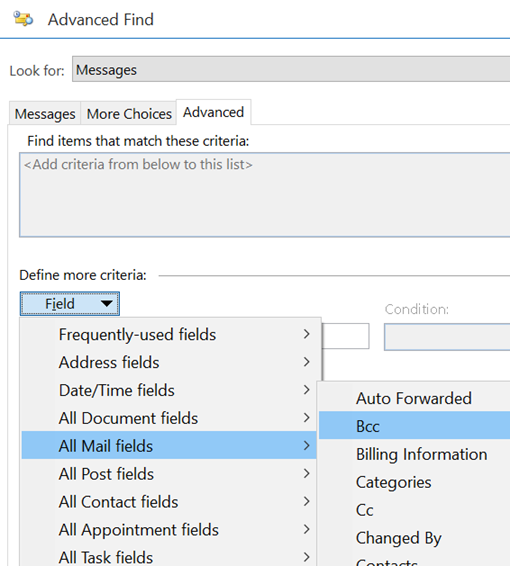
The first couple of tabs on the Advanced Find dialog let you search for mailbox items that fit some common criteria – but the third tab is a window into how Exchange stores and categorises messages, appointments, tasks etc.
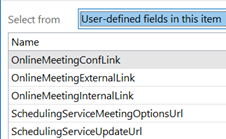
Aside: most apps use CTRL+F to invoke Find – try it in Word, Excel etc – but in the mail client, CTRL+F forwards a message instead. Find out why, here. The idea here is that you can build a query based on properties of messages – and when you select the Field from the extensive drop-down list, it would let you choose appropriate filters (some, like Flag Status or Receipt Requested would only have a couple of possible values, but others would let the user enter text, date or numeric filters). Not all of the fields are used for much these days – eg InfoPath Form Type harks back to the days when the now-defunct InfoPath could be used to create mailable forms – but having a poke around in Advanced Find can give a curious user some insight into how Exchange and Outlook organises their data. |