One of the most profound changes in the way most people use the internet has been broadening out to using a variety of devices. As well as having a selection of laptops, phones and tablets, people will surf across them all the time – from playing with a phone while watching TV, to reading an article or book on a larger-screen slate as well as working on a regular laptop or desktop. Browsers have added functionality to smooth the transition, but most people are probably unaware.
One of the most profound changes in the way most people use the internet has been broadening out to using a variety of devices. As well as having a selection of laptops, phones and tablets, people will surf across them all the time – from playing with a phone while watching TV, to reading an article or book on a larger-screen slate as well as working on a regular laptop or desktop. Browsers have added functionality to smooth the transition, but most people are probably unaware.
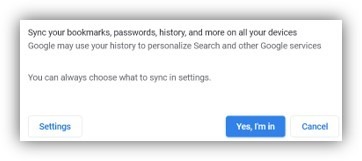 You’ll typically be offered the chance to sign-in and sync your favourites, history and passwords across any other device that you’re using when running Edge or Chrome. If you’re browsing across multiple PCs, one way to easily pick up where you left off would be to go into the browser’s history and revisiting sites browsed from current or previous machine, or use Favourites/Bookmarks or Edge’s Collections.
You’ll typically be offered the chance to sign-in and sync your favourites, history and passwords across any other device that you’re using when running Edge or Chrome. If you’re browsing across multiple PCs, one way to easily pick up where you left off would be to go into the browser’s history and revisiting sites browsed from current or previous machine, or use Favourites/Bookmarks or Edge’s Collections.
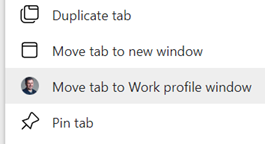
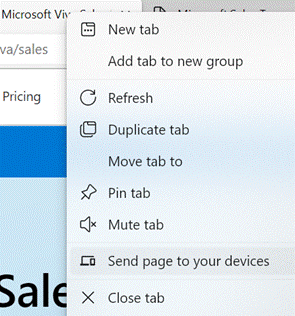 Edge gives you a simple way of sending a currently-viewed tab to another PC or a mobile device – right-click on the browser tab and choose from a list of other devices that you’re signed in on. You’ll then see a near-real-time notification on the other machine that the page has been shared with you.
Edge gives you a simple way of sending a currently-viewed tab to another PC or a mobile device – right-click on the browser tab and choose from a list of other devices that you’re signed in on. You’ll then see a near-real-time notification on the other machine that the page has been shared with you.
 On phones and tablets, if you’re also using Edge and signed in, you’ll see a Send to Devices option on the browser menu, so you can fire links straight to your PC.
On phones and tablets, if you’re also using Edge and signed in, you’ll see a Send to Devices option on the browser menu, so you can fire links straight to your PC.
There are other options, too – the browser menus in both Chrome and Edge have a Share option that lets you send a link to another application, send via Bluetooth to nearby devices of other types and more.
 If you don’t yet have enough toolbars in your life, you could look on the Edge Sidebar, at the new Drop feature, which lets you transfer snippets of text or whole files between browsers on multiple PCs or mobile devices.
If you don’t yet have enough toolbars in your life, you could look on the Edge Sidebar, at the new Drop feature, which lets you transfer snippets of text or whole files between browsers on multiple PCs or mobile devices. 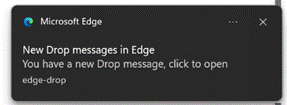 It might be the quickest-yet way to send a photo from a phone to your PC, where received files are dropped into the Downloads folder and stored in OneDrive for other devices to access.
It might be the quickest-yet way to send a photo from a phone to your PC, where received files are dropped into the Downloads folder and stored in OneDrive for other devices to access.

![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0024_thumb.gif)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0044_thumb.gif)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0064_thumb.gif)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0084_thumb.gif)
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0104_thumb.gif)
![clip_image012[4] clip_image012[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0124_thumb.gif)





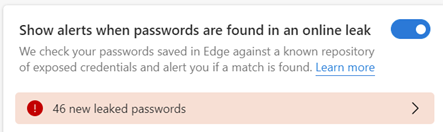
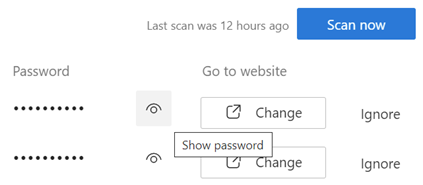
 There are a variety of ways to zoom into content on your PC, maybe so you can read the tiny text or perhaps look for details in an image. If you have a
There are a variety of ways to zoom into content on your PC, maybe so you can read the tiny text or perhaps look for details in an image. If you have a 
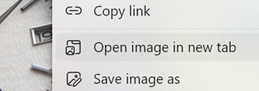 open it in a new tab, thus freeing the graphic from the strictures of the page it’s on and allowing you to zoom in as you please. In some cases, the image you see here will be higher in resolution than the one which was on the page, due to the aforesaid scaling (especially true on eBay images, where often the source is many times larger than the view eBay presents). Even simpler, you may find that clicking on the image on a web page will open the full-size version of it, and that will allow you to zoom in even further.
open it in a new tab, thus freeing the graphic from the strictures of the page it’s on and allowing you to zoom in as you please. In some cases, the image you see here will be higher in resolution than the one which was on the page, due to the aforesaid scaling (especially true on eBay images, where often the source is many times larger than the view eBay presents). Even simpler, you may find that clicking on the image on a web page will open the full-size version of it, and that will allow you to zoom in even further.