|
Of course, many of us know AI as a term used to refer to a host of related technologies, such as speech and natural language recognition, visual identification and machine learning. For a great example on practical and potentially revolutionary uses of AI, see Dr Chris Bishop’s talk at Future Decoded 2018 – watch day 1 highlights starting from 1:39, or jump to 1:50 for the example of the company using machine learning to make some world-changing medical advances.
One simple example is image searching – if you upload photos to consumer OneDrive (directly from your phone perhaps), the OneDrive service will now scan images for text that can be recognized… so if you took a photo of a receipt for expenses, OneDrive might be able to find it if you can remember what kind of food it was.
More AI goodness is to come to Office 365 and OneDrive users in the near future – automatically transcribing content from videos stored online (using the same technology from the Azure Video Indexer and Microsoft Stream), to real-time PowerPoint captions. Watch this space… and mind the robots. |
Category: Windows
Tip o’ the Week 458 – Grabbing pictures from websites
|
Legitimate examples might include things like downloading a company logo from its website so you can include it in a PowerPoint slide; try going to just about any major company site and you’ll probably find it’s not straightforward to save the image file. Ditto all sorts of clever pages that might stop you simply saving the picture to your PC.
If you want to grab the actual URL for an image on a web page, the The Inspect Element funciton in browsers is designed to help web page debugging; it’ll let a user or designer jump straight to the section of a web page’s source, and inspect or even modify the code behind the page.
Look for the src= part, double-click on it and you’ll see the URL of the image in an editable text box, meaning you can easily copy that to the clipboard and get ready to paste it wherever you need it Using a search engine Of course, there may be easier ways to get an image – using Bing or Google search, for example. Bing is actually quite a bit better in this regard. When you click on an image in the results from Bing’s Image search, you’ll see a larger preview of the picture along with a few actions you can take – like jump to the originating page; search for other sizes of the same image; use Visual Search to run a query on just some selectable portion of the image; or simply just view it in the browser, thereby opening just that image and showing you the direct URL to it. In the case of both Google and Bing, if you click on “Share”, then you’ll get a link to the search result of that image rather than the picture itself – so if your plan is to embed the image in another web page or upload it to some other place, then you’ll be frustrated.
Simply choose Upload picture, paste in the URL of the logo you want to use and you’re off to the races. Figuratively speaking, anyway. You might have to jigger about with the proportions of the image by downloading it first and editing it elsewhere, as the image will need to be more-or-less square. Built-in icons in Teams appear to be 240×240 pixels in size so you could try to target that if you’re resizing. |
Tip o’ the Week 457 – Clipboard improvements
 Windows 10’s latest update – the October 2018 Update – has now started rolling out again, after a series of issues reported by some users about data going missing. Here’s how to get it if you don’t have it already and don’t want to wait until it trundles along via Windows Update. Windows 10’s latest update – the October 2018 Update – has now started rolling out again, after a series of issues reported by some users about data going missing. Here’s how to get it if you don’t have it already and don’t want to wait until it trundles along via Windows Update.
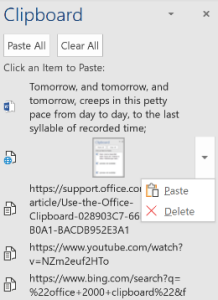
One of the neat new features is a revamped clipboard – something that has been tried a few times before, supporting additional features like keeping a history of what you clip, and/or allowing clips to roam across different machines. This has at times been achieved in standalone apps (eg via The Garage), or through individual apps managing the process – did you know, for example, that Office had a clipboard that supported
In Windows 10 with the October 2018 update (version 1809: to check your version, press WindowsKey+R then enter winver), there’s a new paradigm for managing the clipboard right across Windows applications – and it harks back to the old CTRL-V key combo that is more than 50 years old itself… from ToW #133 (from mid-2012): CTRL-V goes back a loooong way. Its first use was years ago in the “Quick Editor” – aka QED – co-developed by Butler Lampson, one of the giants of computer history, now employed as a “Technical Fellow” in Microsoft Research.
|
Tip o’ the Week 456 – Alexa on PC
|
Amazon meanwhile has brought the Alexa app to the PC, not just on select new machines but for everyone running the latest release of Windows 10. See here to install. This gives you the option of talking to your PC to control the plethora of 3rd party devices that support the Alexa ecosystem, as well as all the other stupid stuff you might ask of Alexa already. Find out more, here. |
Tip o’ the Week 455 – Pin your PMAs
|
Microsoft published a bunch of 3rd party PWA apps directly into the Microsoft Store (eg start with SkyScanner then click on “Microsoft Store” when opened with the Store app itself rather than the web UI), though there haven’t been any new ones for a while. Google is also throwing its weight behind PWAs – so much so, that version 70 of the Chrome browser has support for PWAs that can be installed to look like a desktop app on Windows, so when the PWA is running it hides the browser UI and is launched from either within Chrome directly, or from the traditional Windows app UI.
To look for dedicated PWA resources, check out this list, or look here, here or here. |
Tip o’ the Week 454 – Time Zone Tumult Ahead
|
Many Southern Hemisphere nations have already moved into “summer time”, though a few will make the transition on 4th November. Europe, most of Mexico and parts of the Middle East will move out of DST this weekend, but most of the North America and the Caribbean will “fall back” the week after. See the list of places that currently observes DST and when they transition. This can play havoc with people’s electronic calendars; systems these days generally take notice of time zone changes pretty well and that means the relative times of meetings are preserved, though what this does mean is that a 9am meeting organised in Seattle (and therefore hosted in Pacific Time) will be 5pm for attendees in London this week, but it would be 4pm GMT the week after, then back to 5pm after that, as the US moves clocks back. This topic was covered 3 years ago in ToW #301, and most of the tips contained therein are still valid today. Maybe future generations will stop the winter/summer time flip-flop effect altogether (Californians get to vote on whether to join their neighbours in Arizona, by staying on the same time zone all year, and the EU may stop the practice of changing clocks too). In the meantime, for a few weeks a year, those of us who deal cross-border may need to think a bit more about what the time is in our neighbour’s locale.
One further innovation since the last time this topic was aired, is that Outlook now lets you show a third time zone in calendar if you so desire. |
Tip o’ the Week 449 – Snipping Tool gets the snip
 As mentioned in ToW #447, there are some tweaks coming in the Windows 10 October 2018 update, which might be with us sooner than you think.The old Snipping Tool (not to be confused with the similar screen snipping utility that’s installed if you have OneNote 2016, activated by pressing WindowsKey+S) is going away, and giving way to a new program. And some people aren’t happy about it (in fact, if this was a story which features on the sponsored clickbait tiles on the Edge browser homepage, it’d be described as Microsoft Has a New Trick, and These People are Furious About It…). As mentioned in ToW #447, there are some tweaks coming in the Windows 10 October 2018 update, which might be with us sooner than you think.The old Snipping Tool (not to be confused with the similar screen snipping utility that’s installed if you have OneNote 2016, activated by pressing WindowsKey+S) is going away, and giving way to a new program. And some people aren’t happy about it (in fact, if this was a story which features on the sponsored clickbait tiles on the Edge browser homepage, it’d be described as Microsoft Has a New Trick, and These People are Furious About It…).
If grabbing a free-form selection, once you’ve more-or-less completely made a shape and when you release the mouse button Despite the fact it’s a Modern App and People With Too Much Time On Their Hand Think This… is a bad thing, it’s actually pretty snappy and provides a useful polish to one of the more esoteric but handy features in Windows.
Of course, another method (useful in the preparation of this very note) is to rely on the old PrntScn button, the pressing of which dumps the contents of the screen – floating toolbars and everything – straight into the clipboard. Paste the contents into MSPAINT, then use the Snipping method above to grab the relevant section of your screen grab, and you’re sorted. |
Tip o’ the Week 448 – Sometimes, size does matter
|
Nowadays, with 50 or 100GB mailbox quotas being the norm, most Outlook users don’t need to worry about reducing the size of their mailbox other than to keep it from being too hard to use – a tidy mind and all that. But if you have massive mailboxes, the storage and organisation of all your content may put an unnecessary strain on your PC, so it’s worth taking a few steps to check and clean up if you can. In Outlook 2016, go to the File menu and l … and marvel at a dialog box that hasn’t changed since the earliest days of Outlook, evidenced by the fact it measures size in KB rather than MB or even GB… Limits to be aware of There are some recommended limits that have been given to Exchange/Outlook users over the years – not just about the overall size of the mailbox, but the number of items in certain folders and even the number of folders themselves. See a 2005 post on the Exchange blog here, for example, which advises keeping the item count low on certain folders (< 1,000 items in the Inbox, Calendar and Contacts folder was the recommendation then – also on the Exchange Blog, check out some of the examples in this post for early pioneers of huge mailboxes). In more recent versions of Outlook, though, there are some guidelines to avoid performance problems:
Now, you’re probably not going to have too many folders with more than 100k items though it might be worth checking Sent Items and Deleted Items. Unfortunately, the mailbox size tool above shows you the total size of each folder, rather than the number of items – and if you want to know how many folder you have, you’d need to manually count them in the scrolling list box: not an easy task if you have lots of them. It’s quite possible if you’ve had your mailbox for a while, and you’re a very diligent filer (especially if you use a methodology like GTD or tools like ClearContext), you could inadvertently have more than 500 folders – and if you use AutoArchive, then you could find a lot of them are empty, since the archive process moves the items out into another location but leaves the folder structure behind.
FolderCount to the rescue Here’s an interesting little hobby project – a macro-enabled Excel sheet which cycles through all the folders in your mailbox, tells you how many items are in each one and offers to get rid of the empty ones for you. It can be run in:
Use with caution; though anything that is successfully “deleted” will be moved to Deleted Items first, therefore you’ll need to run it again to actually do the damage (or just empty your Deleted Items… a thought that fills some people with dread). To run it, click on the link above, save the file locally, open it up in Excel and you’ll need to Once you’ve done that, click on the appropriate button to let it run. I’d suggest starting with the top one until you feel brave… *The Thread Compressor tool was made available externally after a time, but the domain disappeared… the actual Outlook Addin is again available here, but you’re a bit on your own as far as installing and using it is concerned… |
Tip o’ the Week 447 – October is usually boring
|
If you get excited about updates to your computer’s operating system, however, October is going to be a bit more interesting, as the next release of Windows – hitherto known as Redstone 5 – will be with us. Read more from MJF, and see a good summary of what’s coming, here.
There’s a great new cloud-oriented clipboard experience that can be enabled (it’s off by default, so no need to get spooked), and there will be an improved screen snipping capability – both examples of the kinds of supposedly small improvements which can make a big difference to anyone with more than one PC. And both of these are features that have been proven using “Garage” projects in the past. The Your Phone app discussed in ToW 442 will be available to all, too. The much-anticipated “Sets” feature isn’t coming this time, though. So keep ‘em peeled over the next few weeks, for the appearance of the October update. Maybe more news will come at Ignite. |
Tip o’ the Week 446 – What’s brown and sticky?
|
A: A stick… Q: What’s yellow and sticky? Yes, the Post-It note (which has gone on to spawn many imitators, sometimes known as just “stickies” or “sticky notes”) was essentially invented by accident almost 50 years ago, by a scientist at 3M who was trying to make a super-strong glue but instead came up with one that didn’t really stick very well but was at least reusable and didn’t leave any residue behind. Of course, the real story is a lot less simple – the product really took more than a decade to perfect, and convincing people that it was a viable business took several attempts, but eventually it went on to be one of the most-bought office supplies in history. The digital equivalent has had decades of evolution too, from a simple note app from the company that brought you Tiny Elvis to the Sticky Notes application that shipped with Windows 7, and innumerable similar apps in the various mobile and desktop app stores. Starting with the Windows Insider “Skip Ahead” community (but soon to roll out wider), the Microsoft Sticky Notes app has been heavily revised, consolidating the multiple windows that would typically be left on your desktop with a single list, and then pop-out notes that feature multiple colours, support for ink, cross-device syncing and more. Keep an eye out for the Sticky Notes 3.0 arrival on your PC. As MJF says, with the same team now responsible for OneNote, To-Do/Wunderlist, and Sticky Notes, it’ll be interesting to see how deeply integrated they get. |












 And it’s
And it’s 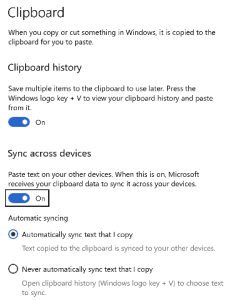
 mechanism is an opt-in arrangement, where you can carry on using the one-hit clipboard as normal, or you can enable history or even cross-device Syncing to allow multiple machines to get the same history, just like browsing history, Timeline etc can roam across different machines if you wish.
mechanism is an opt-in arrangement, where you can carry on using the one-hit clipboard as normal, or you can enable history or even cross-device Syncing to allow multiple machines to get the same history, just like browsing history, Timeline etc can roam across different machines if you wish.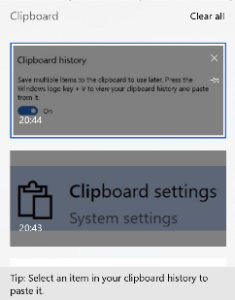 To access the new Clipboard UI, press WindowsKey+V. There isn’t much obvious control over the experience (other than enabling it via Settings).
To access the new Clipboard UI, press WindowsKey+V. There isn’t much obvious control over the experience (other than enabling it via Settings).![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](https://msdnshared.blob.core.windows.net/media/2018/11/clip_image0024_thumb.jpg)








 The new
The new 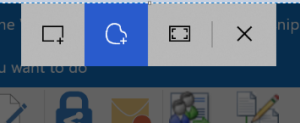 olbar at the top of a greyed-out screen, making it quick and easy to either grab a rectangular portion of the screen, a free-form selection, or the whole screen itself.
olbar at the top of a greyed-out screen, making it quick and easy to either grab a rectangular portion of the screen, a free-form selection, or the whole screen itself. you’ve been holding down, then a large “toast” appears in the bottom right of the screen advising that it’s now in the clipboard. If you click on that,
you’ve been holding down, then a large “toast” appears in the bottom right of the screen advising that it’s now in the clipboard. If you click on that, 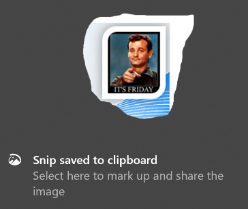 you’ll be launched into the Snip & Sketch app, where you can do various tweaks to your grab, save it, share it and so on. An alternative to the Win+S method of invocation is to go into Snip & Sketch to start with, and initiate a new screen grab from there.
you’ll be launched into the Snip & Sketch app, where you can do various tweaks to your grab, save it, share it and so on. An alternative to the Win+S method of invocation is to go into Snip & Sketch to start with, and initiate a new screen grab from there.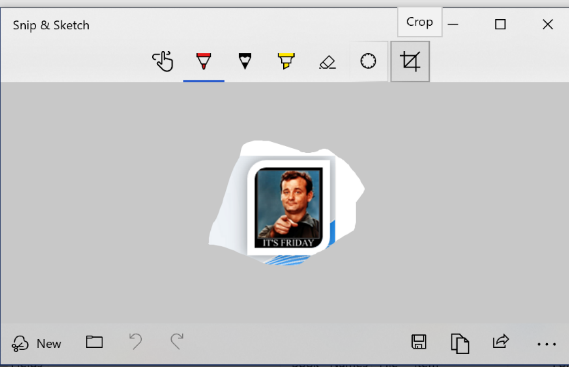 Handy especially if you prepare any kind of training documentation, or you’re stupid enough to send out a weekly tips email to thousands of people for 9 years.
Handy especially if you prepare any kind of training documentation, or you’re stupid enough to send out a weekly tips email to thousands of people for 9 years.






