|
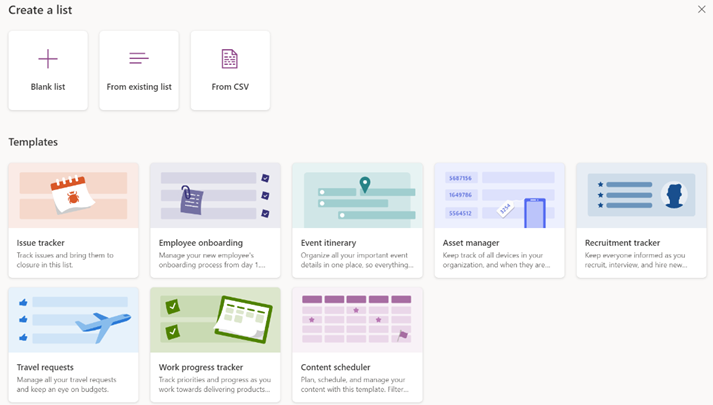
A while back, Microsoft released a new app for Microsoft 365 users called Lists, which was essentially a front-end to SharePoint, itself a staple of the Office 365/Microsoft 365 offering since the beginning, and providing much more functionality than simply a place to stuff documents. The original SharePoint Portal Server 2001 (codenamed “Tahoe”) is nearly old enough to buy itself a beer in its homeland, and relatively advanced logic and custom data validation & handling has been a major part of its appeal for a lot of that time.
Recently, the Lists experience was made available – in preview – for non-M365 users who could sign in with their Microsoft Account. A “lightweight” version of the app, it’s still pretty functional and pitched at individuals, families or small businesses who need to keep lists of things. Taking a slightly different tack, the To Do application is a good way of making other sorts of lists – that could be Tasks or flagged emails as well as simple tick-lists to mark off what needs to be done. In something of an overlap with Lists, To Do can share its lists with other people – think of To Do as primarily for personal use that you might share, whereas Lists is for managing shared endeavours first and foremost.
|
Category: Mobile
616 – Feature Power
|
The path to how new features for Windows 11 will be rolled out is changing a little too. Having previously said that there would be only one Feature Update each year, rather than the spring/fall update cadence that has been with Windows 10 for some time, there are going to be intermediate feature experience packs which will deliver some updates, like the forthcoming Android subsystem which will allow Windows 11 users to install and run a subset of Android apps and games on their PC.
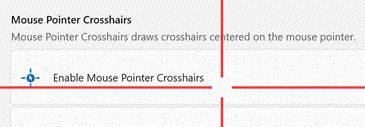
If you want some groovy new features for your PC without grubbing around in the command line or waiting for a future update to arrive, do check out the recently-refreshed PowerToys package. The tl;dr history is that PowerToys started as a collection of side projects built during the Windows 95 days, shipped as freebies for power users to play with. The name was dusted down a couple of years ago to collect up similar skunkworks projects for Windows 10 (and now, 11), and has been updated fairly regularly – though the release version is still way off v1.0. The New PowerToys comprises a collection of addons which will Of particular interest (and most recent) are utilities to do with your mouse – how many times have you tried to find the location of your pointer (especially if you have multiple screens) by waggling the mouse or tickling the trackpad? Press CTRL key twice to Find My Mouse and the screens go dark, except for a spotlight that shines on the current pointer location. There’s a Mouse Highlighter which – when activated via a configurable shortcut key – leaves a little short-lived blob on-screen where you clicked the mouse; great if you’re recording a training video or doing a demonstration.
The PowerToys use a lot of different shortcut keys – some configurable – and also have a handy Shortcut Key guide, which displays common Windows shortcuts; none of those used by the PowerToys themselves, though. |
614 – Good Game, good game!
|
“Wordle” became a synonym (or even an anthimeria) for a “word (or tag) cloud” from Other Wordle sites still exist. In late 2021, another Wordle appeared – a play on the name of its creator (Josh Wardle), a simple word game which has taken the internet by storm. It deliberately only had one round per day (so as to not rob the player’s attention like many other games do), and aims to be free to play and commendably ad-less. If you’d prefer to have your attention stolen so you can repeatedly play the game, try clone Wheeldle instead. Of course, many other word games are available as apps and sites – like Wordle, the word-search mobile app which has been around for years, along with a load of clones of the viral 6-line Wordle web app; they may not be free and may not be free of ads. Apple has already weilded the ban hammer to several Wordle rip-offs. If you’ve not been much of a word puzzle gamer previously but you’ve taken to Wordle, try out Wordament – a venerable app available on mobile devices and Windows PCs alike. It’s also available online. However you play it, you will need to put up with some ads on the way. Or just wait until the following day so you can tell Twitter how your Wordle quest went. Aaerm… |
598 – Start me up
|
Now, Start is a new thing – a relaunch of Microsoft News.
Users of Windows 11 in preview – due to release soon – can see the widgets for news on their task bar, or any users can go to MicrosoftStart.com. If you feel ` reducing the clickbait and garbaj, you can tune the sources and types of news you’ll receive and save the settings with your Microsoft Account. Apps are available for iOS and Android, on the web, the Windows taskbar / widgets, and on the new tab page on Microsoft Edge (like it or not). One notable absence from the announcement? The Microsoft News app for Windows. Install it while you still can. |
590 – OneNote Tagging
|
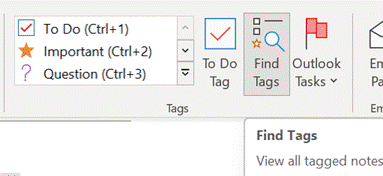
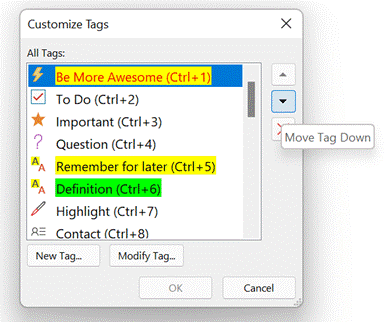
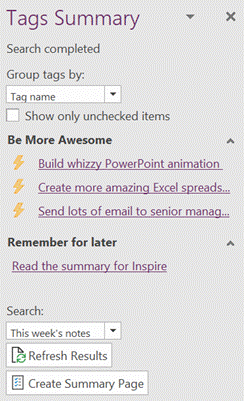
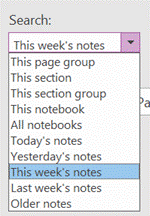
Try using the Search filters at the bottom to restrict the results set, so you only show tags within a given notebook location or across all your notebooks, but for a specific time.
In the OneNote for Windows 10 store app, you can search for Tags but custom ones created in the desktop app don’t appear in the Tags list when editing a page. Only a handful of tags are initially offered in the store version, and if you add a custom one it’s still possible to press CTRL+n to use it, but you need to count where your tag is in the list as it doesn’t show you the shortcut. Custom tags added in the store version don’t appear in the tags list of any other client though do sync across other devices, to some degree. Given the slight rough edges between the versions if you routinely open the same notebook in mobile, web and store/desktop apps, then Tags may not prove so useful – but if you tend to stick to a single UI – especially if it’s the older desktop one – then it’s worth exploring how custom tags could help you organize your stuff. |
580 – Let’s Lens
|
The “Office Lens” app was originally produced for Windows Phone before being ported to iOS and Android. Later, a PC version came along but with the death of Windows Phone it hardly seemed worth keeping going, since scanning docs and business cards etc is so much easier from a handheld device. As a result, Office Lens on the PC is now gone – dispatched at the end of 2020; if you had installed it previously, you could still use some of its functionality, though the smarter online services that sat behind it are no longer available.
There are tweaks to the algorithms used to detect edges of documents when scanning pages or turning a receipt snapped at an angle into a square-on image. It’s not always perfect, but you can drag the apices to tidy up the process, and save pages as images on their own or multiple pages of a document into a single PDF file, straight to OneDrive or local on the phone.
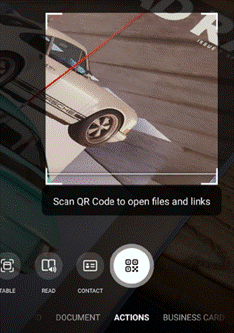
Similarly, barcode reading just brings back the number, whereas some other apps will provide a bit more context – Lightning QR Reader for Android, for example, can read any text encoded in a QR code and will also give some more details for barcodes, like decoding ISBN codes on books to let you search for more info on that specific title. Still, Lens provides a neat & quick solution for scanning or capturing all kinds of info.
|
562 – Connect your phone to Your Phone
|
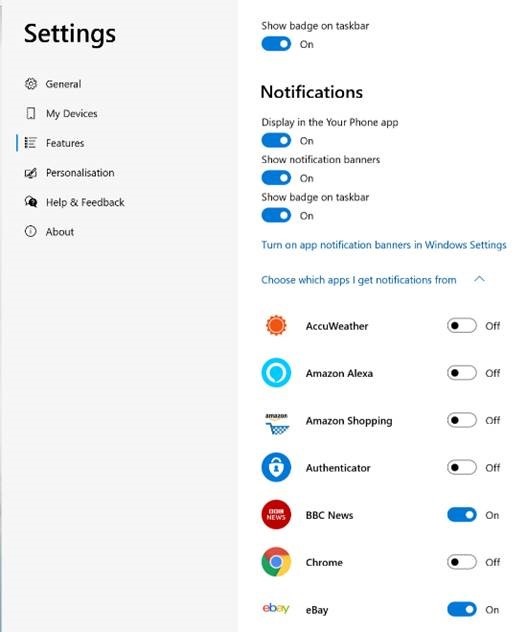
If you’re an iPhone user, the connected experience is somewhat watered-down and achieved in a different way, and is mostly about syncing content and continuing web browsing from your phone to your PC. Thank the differences in Android vs iOS ecosystems for that… For various Samsung phones and the Surface Duo, you can also control and mirror apps from your phone on the PC as well as transfer content. If you have a phone with the shiniest of shiny Android 11, you may be able to treat mobile apps just as if they are Windows apps – pin them to Start menu, run them in their own window on the PC etc. See more here. For most other Android devices, you can’t yet do the mirroring within the Your Phone experience, but you do get to share app notifications on your PC (so you’ll get “toasts” in Windows for WhatsApp etc), exchange photos and files quickly and easily, manage messaging and even, should you want to, take and make calls on your PC.
If you’re going to enable notifications, be careful – you’ll want to go through the list of apps that are on your phone, and only allow the ones you really need, or you’ll be getting a blizzard of unwanted toasts on your PC, assuming you’re not in Focus Assist mode. Perhaps the best feature on Your Phone is the rapid ability to copy photos – without having to send them by email or wait for OneDrive to sync them. Using Your Phone, you can copy the file immediately to your PC, or just browse the photos on a larger screen and possibly screen grab bits of interest to insert into documents or emails. Sadly, what it won’t let you do is manage the photos easily, like delete the garbage… Still, it’s free and it’s potentially useful for anyone with a Windows 10 PC and an Android phone – so definitely worth a look. For more info on how to use and troubleshoot Your Phone, see here. |
556 – Using MFA more widely
|
So 2FA – or its cousin, Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – is a better way to secure things, as a remote system can validate that the user knows something which identifies them (their username & password, secret phrase, date of birth etc etc) but also has something that identifies them too; a security token, smart card, digital certificate or something else that has been issued, or even just a mobile phone that has been registered previously with whatever is trying to validate them. Although such systems have been around for a while, the average punter in the EU has been more recently exposed to 2FA through a banking directive that requires it for many services that involve transfer of funds, setting up payments or even using credit cards. In some cases, the tech is pretty straightforward – you get a SMS text message with a 6-digit one-time code that you need to enter into the mobile app or website, thus proving you know something (you’re logged in) and you have something (your phone), so validating that it really is you. Or someone has stolen your phone and your credentials… MFA is stronger than 2FA, as you can combine what you know and what you have, with what you are. An example could be installing a mobile banking app on your phone then enrolling your account number, username & password; the know is your credentials, and the have is a certificate or unique identifier associated with your phone, as it’s registered as a trusted device by the banking service that’s being accessed. Using your fingerprint to unlock the app would add a 3rd level of authentication – so the only likely way that your access to the service (for transferring funds or whatever) could be nefarious, is if you are physically being coerced into doing it. 2FA and MFA aren’t perfect but they’re a lot better than username & password alone, and Microsoft’s @Alex Weinert this week wrote that it’s time to give up on simpler 2FA like SMS and phone-call based validations, in favour of a stronger MFA approach. And what better way that to use the free Microsoft Authenticator app? Once you have Authenticator set up and running, It’s really easy to add many
In the Microsoft Authenticator app itself, add an account from the menu in the top right and then choose the option that it’s for “other” – presuming you’ve already have enrolled your Work or school Account (Microsoft/Office 365) and your Personal account (MSA, ie Outlook.com etc). After tapping the option to add, point your phone at the QR code on the screen and you’re pretty much done; you’ll need to enter a one-time code to confirm it’s all set up – rather than getting an SMS, go into the list of accounts in the Authenticator app home screen, open the account you’ve just added then enter the 6-digit code that’s being displayed. This is the method you’ll use in future, rather than waiting to be sent the 6-digit code by text. As you can see from the description, there are lots of other 3rd party apps and websites that support MFA using authenticator apps –
|
553 – Android Autobahn
|
The main Android Auto app can either be run manually or set to start automatically when the phone connects to your car’s Bluetooth system. The app displays a simplified arms-reach or voice-driven UI, showing navigation, telephone and music apps, and the settings allow for a good amount of choice – Waze or Google Maps, Spotify or Amazon Music etc. Assuming you’re There are 120-odd Android Auto compatible apps, so even if you don’t see their UI on the main menu, you could respond (with voice) to incoming messages on WhatsApp, or choose to listen to podcasts with Stitcher as one of several interchangeable “music” apps. If your car does support Android Auto (check compatibility here) then it might take a bit of experimenting to understand how to connect it and how to get the car’s display to show the app outputs, though the results are largely the same as what you’d see if you just ran the host Android Auto app on your phone screen directly. You might be able to replace the satnav system in an older car with one which does support Android Auto – see here for some ideas – as aftermarket satnavs are increasingly simple, ditching a CD/DVD player and maybe not even having a radio tuner – perhaps all you need in your car stereo is a 7” screen to which your phone connects, and an amplifier. Some retro-fit satnav systems use Android as their own OS, and offer a whole host of Carlos Fandango features for little more than the cost of a maps update for an older in-car system. |
547 – I Stream a stream
|
Streaming technology has risen with the availability of high-speed, low-latency internet access, allowing users to play on-demand – rather than watch or listen at the time a broadcaster decides – and is wiping out the need to record live TV to watch later, maybe even obsoleting the concept of broadcast TV. Perhaps the next vanguard is the gaming industry – as Microsoft and Sony get ready to launch next-generation consoles, buying a disc-based game to install and play will soon feel as old-hat as going to Blockbuster to rent a VHS for the night. Streaming games on-demand as part of a subscription service may be norm, rather than buying and owning a title outright. The console isn’t the only destination, though – streaming to mobiles is on the way.
Back in the workplace, streaming takes a different form, from virtualizing and delivering applications on-demand to running whole desktops somewhere else and displaying the output on a remote screen, not unlike the old mainframe/terminal model. And of course, there’s streaming of other types of media besides applications.
If you miss that, or weren’t at the meetin Unfortunately, you won’t get paid millions of dollars and given tons of free stuff but you might get some sort of corporate kudos and recognition.
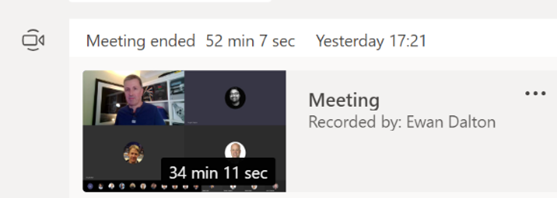
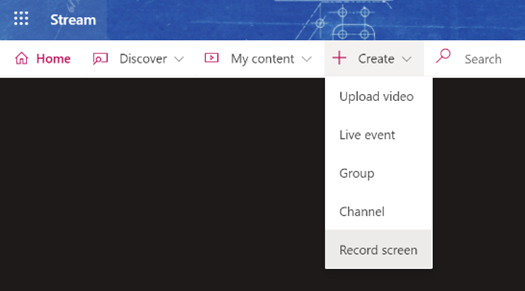
It’s not just for storing recordings of meetings in the hope that people who couldn’t be bothered to turn up the first time will somehow tune in to watch the re-run; you can create new content and upload that for your colleagues to view, too. You could use the Record a Slide Show feature in PowerPoint, to make an (editable) recording of you giving a presentation and publishing it, or if you’re just looking to do something quick and easy (up to 15 minutes in duration), you can even kick off a screen-recording (with audio and video) from the Stream site directly.
Maybe record it to a VHS tape and post it to them? |