Obscure Computer Science theory had an obsession with “object orientation” some years ago; both a technique in how applications are written but also design thinking on how they might be used. Sensei Steve Jobs, while walking the earth before coming back to save Apple, had a famed obsessions for design and rooted his NeXT computer on an object-oriented approach. The NeXT Cube itself was arguably ahead of its time, but in 1990 cost a cool $10K (that’s about $25K in today’s money). There were few takers, though the odd geek still gets excited to pick them up 2nd hand.
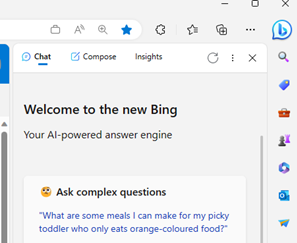
An example of object orientation in user interaction is that you go to a thing you want to work with, rather than a tool with which you want to work. Elements of this are all over UX in Windows, like going to a document in Explorer, and it lets you open, edit, print, etc. Most people will still go to Word and open a file from there; that’s why the Most Recently Used list and Search features exist.
To start something new, you’ll likely open your app of choice then use it to create a file or open an existing one. When did you last go to SharePoint and use the New -> menu option to create a document in situ, much less a OneNote notebook? Exactly.
There are other places where things are less cut and dried: you might open a notebook like OneNote, Evernote, Notion etc, and start taking notes on a thing you’re working on. Or you might want to be in the flow – in a Teams meeting, or viewing a document on which you want to make some side notes – and it makes more sense to bring the notepad to the side and ideally keep the context so when you revisit that document or that webpage, you’ll (optionally) see the notes you had previously.
Progress is not forthcoming
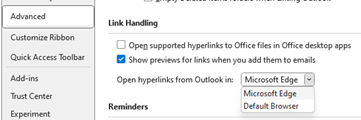
Sadly, as apps evolve some features are sacrificed perhaps because telemetry tells the developer that they’re not much used, or they just decide that newer things are more important. One key villain in this regard is the “new” (Chromium) Edge browser, which left behind many of the features of the old(“Spartan”) Edge, which might not have been much used but then neither was the old Edge. The dev roadmap appears to focus on more ways to inject adverts and to jam Bing services and Copilot into everything, than to actually make the browser as useful as the one it replaced.
Linked Notes
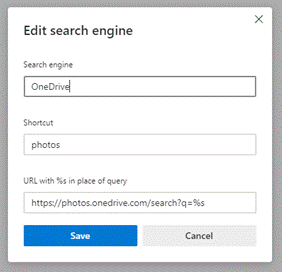
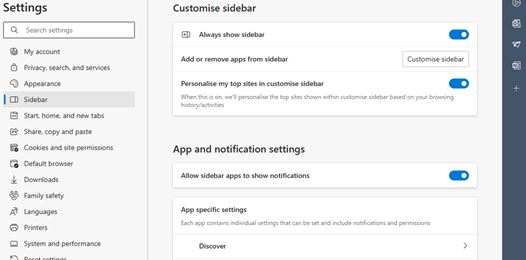
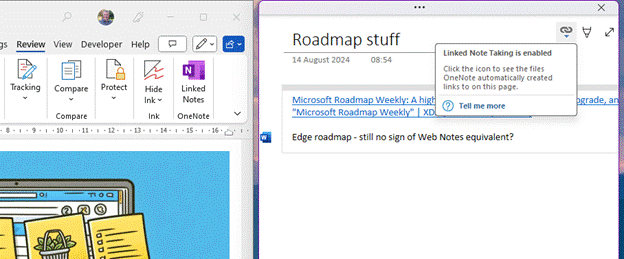
As covered 18 months ago on old testament ToW 683, OneNote has the capability to be docked to the side of whatever other window is being used, and in some cases, maintains a link to the document that is in the main window.
You’d create the page you want to make notes on in OneNote, and when Linked Notes are enabled, it will tie back to the Word etc doc you were using in the other window. That way, if you re-open the notes in OneNote you’re only a click away from pulling up the document they relate to.
If you later go to back to it in Word, however, or open the doc directly from Explorer, there’s no obvious way to bring up the notes you were taking, without going to OneNote, finding the page you took the notes on, and perhaps docking the window again. Even the Linked Notes option on the Review menu doesn’t quite work as expected – it’s for establishing a new link, not reanimating an old one.
This is an example where true object orientation would work well – you’d open the Word doc which you had linked to OneNote, and you’d automatically see the notes in a sidebar.
Remember Internet Explorer?
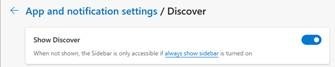
Even ye old IE had an option of being linked in OneNote so you could take notes on a page you were viewing. Sadly, Edge has torched this feature – along with Reading List and one of the more helpful and semi-OO feature, which didn’t use OneNote but was still potentially handy…
Web Notes RIP
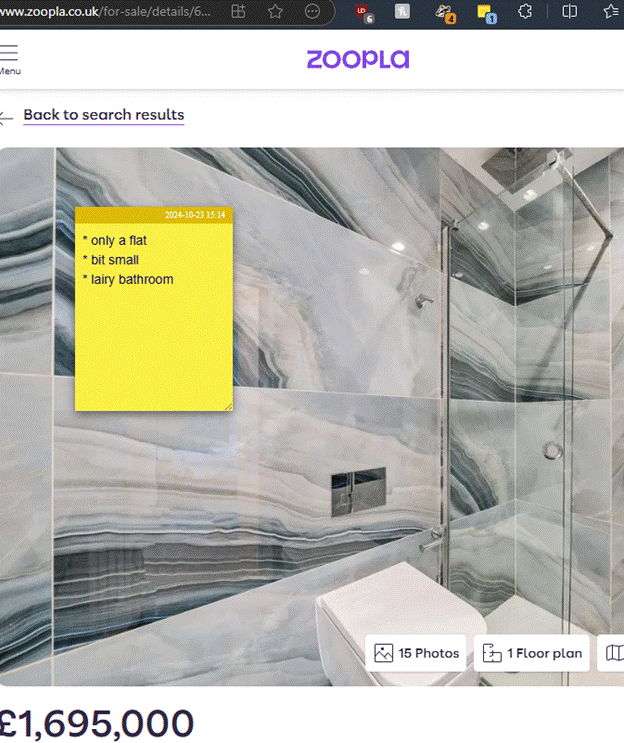
Web Notes was a feature of Old Edge, for jotting down simple notes on whatever page you were viewing, and the next time you visited that same page, the notes would be shown alongside.
Imagine if you were looking to buy a house or pretty much any other major piece of shopping; whilst conducting research, you might browse to several properties of interest and could make some notes about each one – near a good school but close to a busy road, nice rear garden, high crime area down the road, neighbour has planning permission to build a house in their back yard…
It could be so useful to jot the notes as you go and have them presented again if you happen to revisit the same page in future (so you remember you’ve already looked into it). If you could later see a list of every note you took, with a link back to its source, so much the better.
Sadly, there is no way to do this in Edge, without relying on extensions. There are many out there but none really hit the brief well – if you find a better one, please do mention in the comments below.
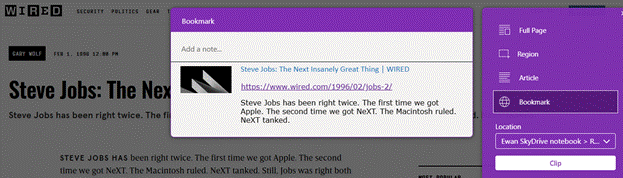
The OneNote Clipper is worth a look if you want to keep a list of notes with links back to pages, but is old school in that you’d go to OneNote to find that list and then see which pages you had commented on, rather than the more Object Oriented approach of viewing a page and having the notes offered to you.
Perhaps the extension which comes closest to the functional requirement (even if it doesn’t win many prizes for looks) is Note AnyWhere, available from the Chrome store (and can therefore be installed on both Chrome and “new” Edge).
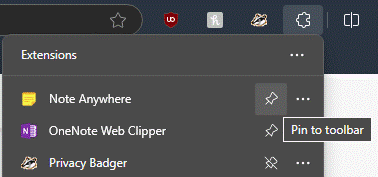
For ease of use, after installation, click the Extensions icon on the toolbar and Pin the Note Anywhere icon to the toolbar, after which taking notes on a new page is only a couple of clicks away. When you next visit a page, previous notes will be displayed (or you can choose to just show a number on the toolbar by the icon, to show how many notes you’ve made).
It would be nice to have some simple formatting, and searching previous notes is a little clumsy (requiring you to sign up and sync with the developer’s web front end), but for a free app that doesn’t (yet) nag you to subscribe for extra functions, it’s not half bad.
PS – Remember, this weekend is when Europe (mostly) ends Daylight Saving Time, meaning next week could see clashing of meetings arranged with international attendees, before North America catches up on 3rd Nov. New Zealand and some of Australia has already made the leap.
This topic has been covered ad nauseam on previous ToWs … spring forward, fall back…

![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0026_thumb.gif)
![clip_image004[6] clip_image004[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0046_thumb.gif)
![clip_image006[6] clip_image006[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0066_thumb.gif)
![clip_image008[6] clip_image008[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0086_thumb.gif)
![clip_image010[6] clip_image010[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0106_thumb.gif)
![clip_image012[6] clip_image012[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0126_thumb.gif)
![clip_image014[6] clip_image014[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0146_thumb.gif)
![clip_image016[6] clip_image016[6]](http://www.tipoweek.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/clip_image0166_thumb.gif)