Many people rely on email for their work, and in some cases the inbox and calendar are the primary tools they use. Gen Z’ers might put up a struggle on entering the workforce, preferring to commune via instant messaging or Tik Tok, but for the most part we know that email isn’t going away. Unless you have an alternative product to sell, that is.
The Outlook application that comes with Microsoft 365 and Office suite has been with us since 1997, but can trace some of its roots back some years before that. Students of history may want to delve into the writings of ex-Office supremo (who went on to bring Windows 8 upon the world), Steven Sinofsky, as he revisits some of the tensions between and the decisions being made by the various development teams. There’s a good one on Outlook’s gestation, or the one where BillG gets presented with the idea for the Office Assistant: 042. Clippy, The F*cking Clown.
In a trope briefly discussed last week, we all know how Microsoft has historically loved to use the same name for wildly different things. “Outlook” is one such case – at various times, the core application which has had quite different capabilities during its growth (especially the difficult second album version, Outlook 98) and the name was associated with a whole slew of other products and/or services.
In the Windows 95 / Internet Explorer 3 days, there was a free app called “Microsoft Internet Mail and News” which combined internet email – POP3, IMAP4 – and the long-dead USENET newsgroup infrastructure based on the NNTP protocol. This was rebranded as “Outlook Express” even though it had nothing to do with the main Outlook application; the actual executable file for Outlook Express was still MSIMN.EXE for its whole life…
[Outlook Express … the solution for all your messaging needs…]
The Exchange Server that sat behind much corporate email added a web view of your mailbox back in 1996, called Exchange Web Access, later renamed Outlook Web Access and then Outlook Web App. As the functionality developed, so the old Hotmail.com service was rebranded Outlook.com, and the functionality of Outlook Web App for Exchange users and the free Outlook.com web client converged to a degree, as Outlook.com was moved to the same Exchange-based Microsoft 365 infrastructure.
Then there’s the mobile Outlook apps – Microsoft acquired email and calendaring companies Acompli and Sunrise Calendar, and folded their stuff into the highly-regarded Outlook mobile applications for iOS and Android.
Finally, when Windows 10 released, there were built-in Mail and Calendar applications; in fact, it was the same application under the hood, but it could be started with different criteria which would set how it looked. This app is still available in the Windows Store and came with OG versions of Windows 11. If you delve back to August 2018 and Tip o’ the Week 445 – Finding Modern App names, you’ll see how to find out what “modern apps” are really called within the system; as it happens, under the hood, the Mail and Calendar app was … ms-outlook.
One Outlook to rule them all
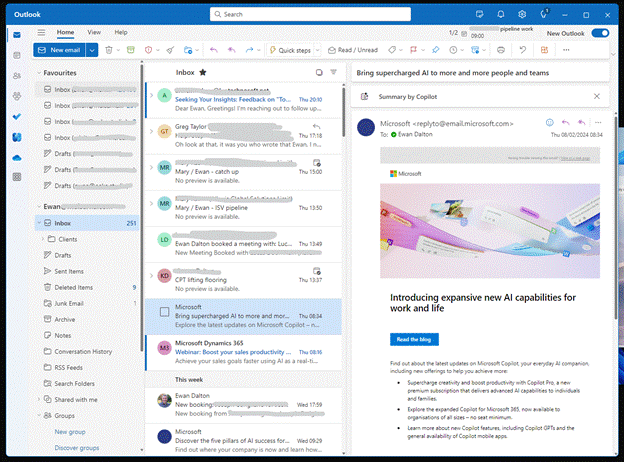
There has been a long held dream in Microsoft of having a replacement for the sometimes creaky old PC Outlook application and the Windows 10/11 Mail & Calendar app, to bring them together under a shiny new application. Sometimes known as “Project Monarch” or “One Outlook”, this new version will use web technologies to effectively be running Outlook Web App but with offline capability, on your PC or Mac.
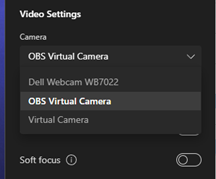
Spot the difference? The New Outlook above has lots of mail accounts added with different inboxes etc pinned to Favourites. Here’s the same primary mailbox in Outlook Web App: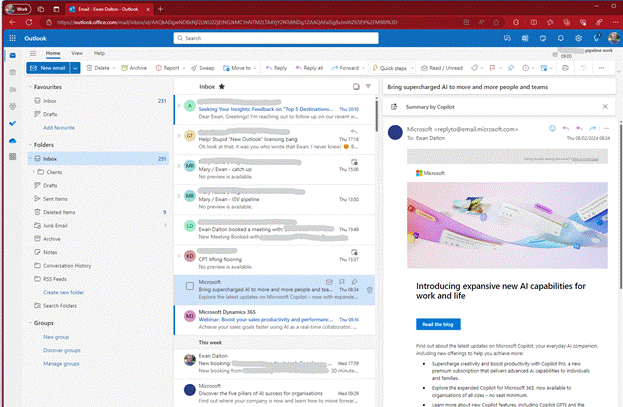
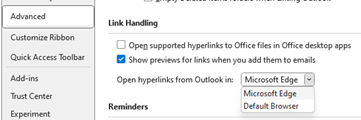
The New Outlook for Windows has been available in preview for a while, and you might be getting nagged to migrate from Windows Mail to try it out, or if your M365 administrator hasn’t switched off the prompt, you could even be getting it in full-fat Outlook.
Having been in Preview for a while, Microsoft announced in September 2023 that this new client is now generally available, and was to be pre-installed on latest versions of Windows 11. By the end of 2024, the old Mail & Calendar apps on Win10/11 will no longer be supported and won’t be available in the Store anymore. It could be a long time coming to migrate desktop Outlook users to the new-fangled version, but the signalling is saying it’s happening someday.
By all means, have a play with the New Outlook – it’s actually pretty good, if you don’t get 10,000 emails every day; in fact, if you have several accounts, it does a better job of keeping on top of them all than old Outlook does (though, arguably, not as well as Mobile Outlook, which lets you see a single Inbox view of all accounts). If you decide to go for it, then you’ll still have access to the Old Outlook app as well (should you need it), and if you’re moving from Windows Mail to New Outlook and don’t like it then the move back should be smooth too.
But currently, there is a gotcha. And it’s the cold hand of license enforcement mistakenly stopping play.
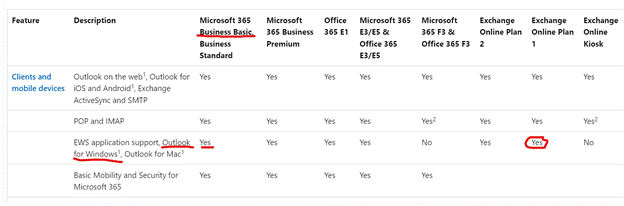
Users of certain M365 subscriptions – Business Basic, or Exchange Online Plan 1 as two examples, are being blocked from using the New Outlook as their license supposedly doesn’t allow it. There is a confusion having a license for a piece of software, and having the rights to use your software against a separately licensed service.
If you look at Compare All Microsoft 365 Plans, you’ll see that Business Basic include “Web and mobile apps only” for Outlook; another way of putting that is “you don’t get the Office applications on your PC or Mac” by buying that subscription. But what if you had the actual software already, through another route? If you have a M365 Family subscription, you can install the Office apps on 6 machines, and there’s nothing stopping you from connecting to a separately-paid-for M365 Business Basic mailbox from your legitimately-licensed Outlook application.
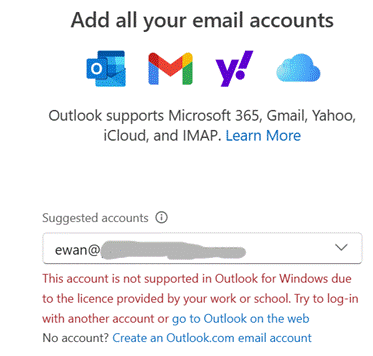
But New Outlook thinks differently. Trying to add a low-cost M365 mailbox gets you an unhelpful error:
Raise a ticket through official support and you’ll be told “you can access your mailbox by upgrading to a premium subscription”. The irony of “Add all your email accounts” is also not lost (especially since free services like Gmail, Outlook.com and Yahoo! seemingly have no problem), but penny-pinching paid-for Microsoft 365 subscriptions do.
Looking at the Exchange Online Service Description…
The service that is being paid for should allow access from “Outlook for Windows”. Regardless of whether that means the full-fat Outlook app that you have to buy, or the freely available “New Outlook”, this document says you can access those mailboxes. But the New Outlook app is now enforcing something different.
Predictably, there are furious users on the internet. The Powers That Be have been made aware and are trying to think up an appropriate way round the issue, apparently. How about, don’t be a Doofus, Rufus? Excellent!
 Take your average Calculator app; its form has changed little from the desktop calculator on which it’s based, or any Calendar application used for organizing appointments which still follows the idea of a planner or physical monthly calendar.
Take your average Calculator app; its form has changed little from the desktop calculator on which it’s based, or any Calendar application used for organizing appointments which still follows the idea of a planner or physical monthly calendar. How many people born in the 21st century have ever used a
How many people born in the 21st century have ever used a 
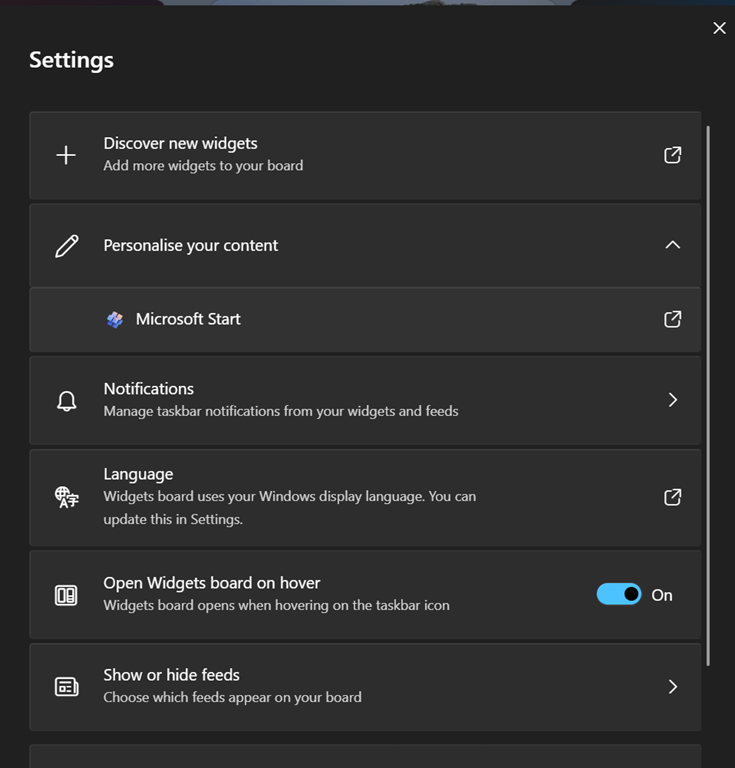

 OK, I said it was gone but it’s just been resting.
OK, I said it was gone but it’s just been resting.