|
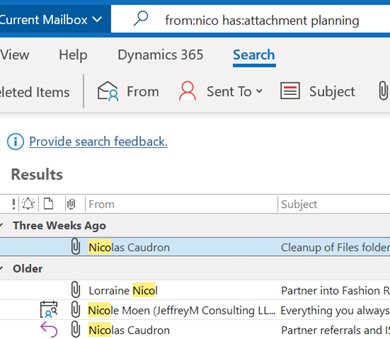
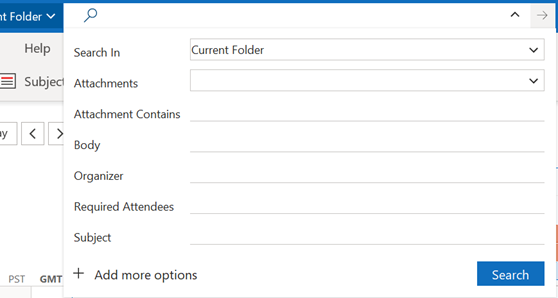
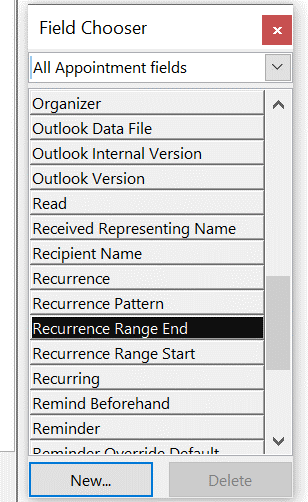
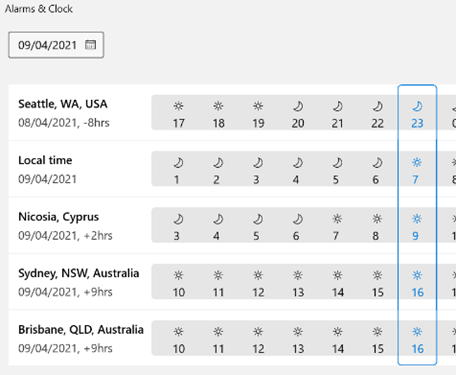
Or has:attachment, which will only show you mails that have other files attached. Combined with a few other criteria, you can filter the results of your search pretty hard, rather than sifting through them. Adding some other smarts like received:”last month” can streamline some more. For more info on search terms, see here. The scenarios our reader posed, though, were specifically around searching in the calendar – eg, do I have a meeting in my calendar with a particular person? Or what recurring appointments are due to expire this month? If you navigate to your Calendar and click the down-pointing arrow to the right of the Search box, it will display a Click + Add more options to bring up a picker that lets you add even more – such as whether the meeting is a recurring one, or if it shows in calendar as Busy or not. Selecting the options builds the query as before, so you can see a variety of defined names – like organizer | organiser (depending on your locale) or requiredattendee:. Coming back to the original question; if you want to find all future meetings in your calendar with anyone called Tony, you could type something like requiredattendee:tony start:>today. And if you want to find out which
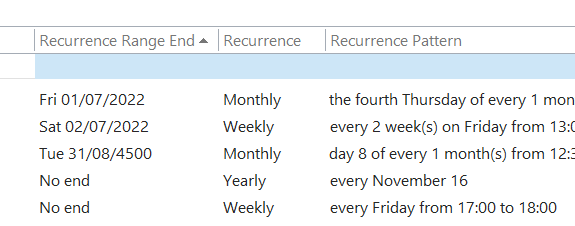
Don’t be alarmed if some of them are due to keep happening until a very long way into the future. We’ll probably have stopped using email by then. History Lesson Before Outlook arrived as part of Office 97, users of Exchange Server had an email client and a separate calendar app (Schedule+; that’s why some diehards still say things like “send me an S+”, meaning send a meeting request). Both would maintain a connection to the server and would chat back and forth, only downloading data when a message or attachment was opened. Although this put something of a penalty on the network, it meant there was no need to cache large amounts of data on a PC hard disk. Outlook replaced both the mail and S+ clients, but maintained the same synchronous connection to the server. Outlook 2003 and Exchange 2003 changed the default model, since PC hard disks were getting much bigger and cheaper, so it made sense to have Outlook deal primarily with a cached copy of the user’s mailbox, bringing all kinds of performance benefits to both end user and to the operators of the server back-end. One really notable improvement was the ability to run fast searches against mailbox data that’s in the cache, rather than having to execute searches on the server. Prior to the cached mode, the best-case scenario for running a search was the server returned messages that fit a particular query asked by the client – mails received this week, mails with FOO in the subject line etc. If the server had indexed the relevant properties (received date, subject etc), it was pretty quick at sending back the results. If the user wanted something more in-depth, it was a punishingly slow process as each message would need to be picked up and inspected to see if it met the query – so searching for every email with a particular word in the message body text would be laborious. Three cheers for cached mode and client-side indexing.
The first couple of tabs on the Advanced Find dialog let you search for mailbox items that fit some common criteria – but the third tab is a window into how Exchange stores and categorises messages, appointments, tasks etc.
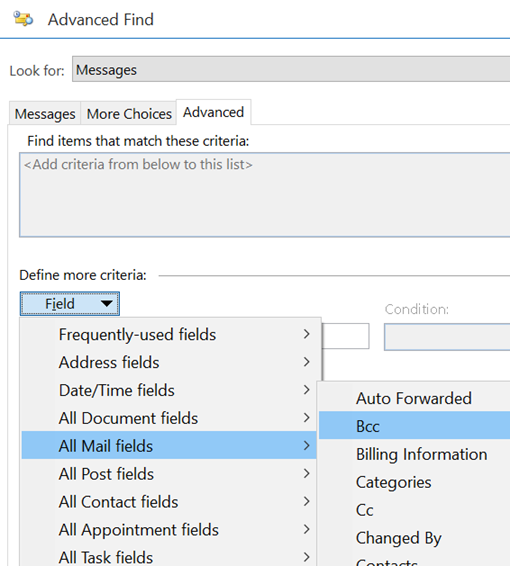
Aside: most apps use CTRL+F to invoke Find – try it in Word, Excel etc – but in the mail client, CTRL+F forwards a message instead. Find out why, here. The idea here is that you can build a query based on properties of messages – and when you select the Field from the extensive drop-down list, it would let you choose appropriate filters (some, like Flag Status or Receipt Requested would only have a couple of possible values, but others would let the user enter text, date or numeric filters). Not all of the fields are used for much these days – eg InfoPath Form Type harks back to the days when the now-defunct InfoPath could be used to create mailable forms – but having a poke around in Advanced Find can give a curious user some insight into how Exchange and Outlook organises their data. |
Month: March 2021
572 – simple OneNote tricks
|
To try to simplify the roadmap somewhat, the app formerly known as OneNote 2016 is now just “OneNote”, and the Store app that shares more of its UX with the mobile and web versions, is OneNote for Windows 10. For more detail on the differences between all the versions, see here. At one point, the plan was to discontinue the more functional desktop app, and shift development to the simpler Store version, however that plan was rowed back and OneNote (the Office app) will continue to be part of Office, even though it wasn’t installed by default in 2019. The perpetual version of Office (as opposed to the subscription service that is Microsoft 365) will be updated later this year, and OneNote will still be part of that. Probably.
As has been covered on ToW passim (here, here), you can start OneNote from the Run command, by pressing WindowsKey+R then onenote <enter> for the desktop version, or onenote: for the modern Windows 10 version. In the latter, you can also pin particular pages to the Start menu, handy if you want to jump to a particular page of quick notes or ideas.
Or maybe by typing a quick few lines at first, and formatting as a list once you’ve got some text. There are some shortcuts to help that formatting; in both OneNote and OneNote for Windows 10, to quickly select what you’ve just typed, hold the shift key and press the up arrow to grab a row at a time.
To create a table, just press TAB to turn whatever you’ve just typed into the first column, and keep pressing TAB to create new columns, or CTRL+ENTER to accept the column layout and start adding extra rows, or to insert a new row into an existing table. Once have content in your table, you can easily move rows around by simply putting your cursor in the row you want to shift, and hold ALT+SHIFT then use the up / down arrow keys to move that row. Much simpler than faffing about with copy & paste.
You can manually create links to any page by selecting the text you want to hot-link from, and press CTRL+K; then either select the destination in the dialog box, or paste the link to the page (or paragraph) if you’ve already copied that link to the clipboard.
Its big brother, OneTastic, also allows using pre-written Macros to automate tasks like custom sorting of sections and loads more. |
#571 – Save the Daylight
|
If the country or state you’re in observes summer time, then you’re either about to enter (if in the northern half of the marble) or leave it (if southern). To keep us on our toes, this movement back or forth often happens around the world on different dates. To keep us on our toes, some countries have less-than-hour gaps between time zones, and in the past, others have decided to change time zone permanently.
– eg if it’s 2:30am in Iran, then lining Tehran up with the red hand would put both London and Paris at midnight, since they’re both at GMT+1. eh? In October 1968, the UK decided to move to British Standard Time – GMT+1 – all year round. This particular wristwatch was produced between 1968 and the end of 1971, when the practice was reversed – so for a while, it was correct that London would be in the same time zone as Paris and Rome. Except the watch wouldn’t know when Paris and Rome went into summer time, thus putting them an hour further ahead… oh well, never mind. In a global working environment, especially one where everything is done online rather than having people in the same location, the friction of time zones changing has never been more obvious. Usually, you’ll only move through time zones relative to everyone else when you travel – flying across large distances, or maybe just driving across a bridge or dam. But now, a digitally-oriented meeting can shift its time for some of its attendees, relative to the others – depending on where the originator is based.
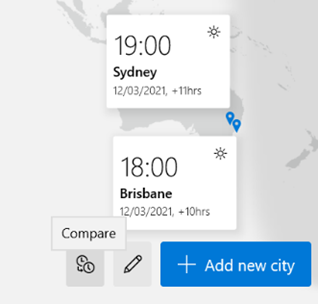
Those parts of the US which observe DST, are due to move an hour forward this coming Sunday (ie March 14th). In common with doing things differently to everywhere else, that brings the US (and Canada) one hour nearer most of Europe for the next two weeks, until the end of March. Much of the southern hemisphere comes out of DST the week after that, so by then Sydney will be two hours nearer London than currently. The impact of this can be seen in peoples’ calendars, when regular meetings somewhat inexplicably start to clash with each other – if a UK organiser set a recurring meeting for 4pm GMT, that would normally compel Seattleites to be there at 8am, but since they’ll be only 7 hours behind for a couple of weeks, that shifts to 9am in their calendar, potentially clashing with some existing 9am Pacific Daylight Time meeting. Conversely, a 9am PST / 5pm GMT meeting as created by the person in the US a few weeks ago, would now start at 4pm in the afternoon in London. Great news if that meeting is a Friday afternoon, as it brings beer o’clock one hour forward. Although Outlook does a pretty decent job of juggling the differences between time zones, there is no obvious way to show what time zone a meeting had been created in (eg show me all meetings that are going to be affected by this shift for the next 2 weeks). A simple trick if you want to check on a specific meeting, is to start a Reply to a meeting you’ve been invited to, whereupon you’ll see the time zone of its creator…
While It won’t help you identify the meetings that are causing the clashes, it might help restrain you from firing angry missives at the organiser of the meeting, if you know what’s causing it. |
570 – Automation for all
|
All were replaced in time with rebranded but otherwise similarly targeted variants:
2020 saw a fast move to hosting everything digitally and for the most part got away with it. 2021 was always going to be different, and the first big do of the year took place this past week – a spring Ignite. When you don’t need to book a conference centre 12 months in advance and get thousands of people to fly in to attend, why not do some of the big events more often or a different time of year? For a summary of what was being announced at Ignite 2021, check out the excellent Ignite Book of News. Charles Lamanna’s keynote on Power Platform highlighted some news around Power Automate – one of the key components of the Power Platform and formerly known as Microsoft Flow, Power Automate began as an online service that could make workflows to stitch together actions that happened across multiple online applications –a new booking alert email to a hotel mailbox could add an appointment to a Google Calendar and send a notification to someone on Microsoft Teams, and so on. Just announced is that the fairly new Power Automate Desktop will be included in Windows 10 and is free to download and use now. This tool brings automation concepts right down to the desktop, allowing any end user to create flows that span multiple apps and services; it’s not unlike an advanced Macro Recorder, where the user can perform a task that is regularly repeated, and the software will keep track of the steps they’re making. With PAD, however, it’s more than just repetition – they can go back and inject data into those steps, like take the email addresses from column B of this spreadsheet and send a specific email to each one, with logic determining what should be different for each message (so a lot more granular than a simple mail merge).
This capability has come about through Microsoft acquiring Robotic Process Automation specialist company Softomotive in early 2020. The impact of RPA is explored when looking at how this technology could remove boring, repetitive tasks thus freeing up clever and creative people to do something better with their time and attention. On one hand, automating processes could be a threat as we’ll need fewer people to do the same things, but a more optimistic view is that it will increase productivity and satisfaction. If you have 17 minutes free, then check out a great TEDx talk on “White Collar Robots”. There’s a great demo of Power Automate technology being used in real-world scenarios, on Microsoft Mechanics. See more videos from the makers on Microsoft Mechanics – YouTube |
569 – Password migration
|
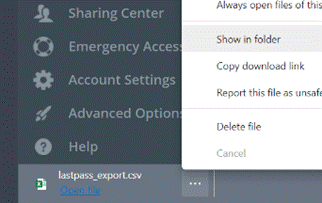
The latest in a line of what-used-to-be-free but is now tightening its belt is LastPass, an excellent password manager that has a lot of users but may end up with a good few fewer. The day after the Ides of March, LastPass Free will only allow use on a single device type, so if you currently use it to sync passwords across desktops and tablets or mobiles, then you need to start paying (and maybe you should) or stick to either mobile or desktop. As soon as the company announced its plans, the web sprung up many articles offering “what is the best alternative to…” type advice. Only a few weeks ago, ToW#561 espoused the virtues of cleaning up your passwords, featuring LastPass and also trailing some features that were coming to an alternative that you might already be using to provide 2 factor authentication on your phone – Microsoft Authenticator. It’s fairly easy to switch to using Authenticator on your device to also sync passwords and to provide the Auto-Fill function which plugs in usernames/passwords not only to sites on your mobile browser but to other apps too. If you already have a load of passwords set up in LastPass or other locations, there are methods to export them and then import the data into Authenticator. In the case of LastPass, you sign into the Vault (either through the browser plugin or directly on their website) and under Advanced Options, select the Export function. It will immediately drop a lastpass_export.csv file into your Downloads folder; be very careful with this file as it contains all your usernames & passwords in clear text.
Now navigate to your Downloads folder and choose the lastpass_export file. It might take a little while to complete, but when it’s done, make sure you go back to the Downloads folder and The LastPass browser extension (like other password managers) remains potentially useful on the desktop as it can help to sync passwords between profiles (eg the Work and Personal profile of Edge, if both have the extension installed and logged in using the same LastPass account), or even between browsers – in the cases you might want to use Chrome for some things and Edge for others. Edge on the PC does have password sync capabilities, though not quite with the same level of flexibility – Edge will let you sync passwords, favourites etc if you’re using a Microsoft Account (eg outlook.com) for your Personal profile, and it may do if you have a Microsoft 365 account for your Work Profile. In a twist of fate, if you pay for a Microsoft 365 Family or a small business environment rather than using the free Microsoft Account, your subscription lacks the Azure Information Protection feature that is required to allow syncing. In which case, a 3rd party password sync feature may be your best option, even if you choose to use Authenticator on your mobile device, and perhaps do a periodic export/import from LastPass to keep your mobile passwords in sync. Or best of all, just install the Autofill extension into multiple profiles (or Edge & Chrome), signing into the extension using the same Microsoft Account, to keep the passwords in sync. Tidy. |
568 – The Race for Space
|
The “space race” continued for some years afterwards (the US had Skylab in the 1970s and built the Shuttle, while the USSR built Mir, the first proper space station), before numerous countries decided to pool resources and build the International Space Station. After unveiling Azure Space in late 2020, the 20th February 2021 – 35 years to the day after the first Mir mission – saw the launch of the ultimate in Edge devices, ensuring Azure reaches the ISS with HPE’s Spaceborne Computer-2. That will be furthest Cloud-Edge computing node until we finally become an interplanetary species, and once again leave the confines of low-Earth orbit. Edge back on Earth If you want to make the most of the space on your screen, you should try moving your Windows taskbar to the side rather than the bottom of the screen – follow the science – as it makes more efficient use of the screen real estate, especially if you have a big widescreen monitor. Open Taskbar settings here and choose Taskbar location. If you’re a vertical taskbar fan, then you’ll like a new feature in the Edge browser, also designed to maximise the use of space – vertical tabs.
By enabling the vertical tabs feature, a single click will show them to the side of the browser window. Click the < caret to the top right of the tab list and they’ll collapse to icons only until you mouse over again, and the full width will be shown.
If you’re using the beta or dev version of Edge, you’ll be able to show the Vertical Tabs button in the Appearance section of the To enable vertical tabs on the current public release, enter edge://flags/#edge-vertical-tabs into the address bar of the browser and switch on the “experimental” feature; you’ll have to restart the browser for it to take effect, but after that point you’re free to try switching the arrangement.
|
567 – Power Teams Apps
|
The artist formerly known as Common Data Service was given a jazzy new name at Inspire 2020, before a sudden realisation that somebody else already owned that trademark, whereupon it was swiftly rebranded Dataverse. In essence, this makes it easy to provide access to a centralised, well-managed, secure data store for pretty much any kind of data, accessible to pretty much any type of app. If you used Power Apps and Dataverse to build line-of-business applications, accessible via browser or mobile clients, there are licensing requirements you’d need to fulfil – but if you want to make a more simplified application that uses Teams as its front-end, then you could use Dataverse for Teams (briefly known as Project Oakdale, using Power Apps under the covers). Licensing for Dataverse for Teams is included in many Microsoft 365 subscriptions – for more details on licensing and what some of the limitations of its use are compared to a full-blown Dataverse environment, see here.
Thankfully, when you need to perform your weekly check on which policies have been updated – or which ones you may have breached this time – they’re only a couple of clicks away.
The Bulletin and Milestones apps are available now. |