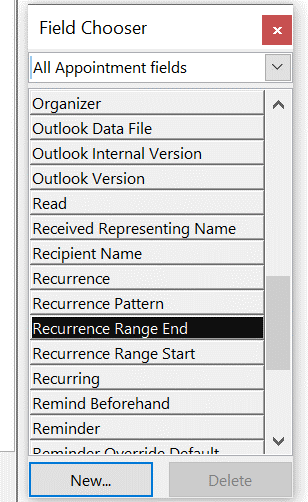
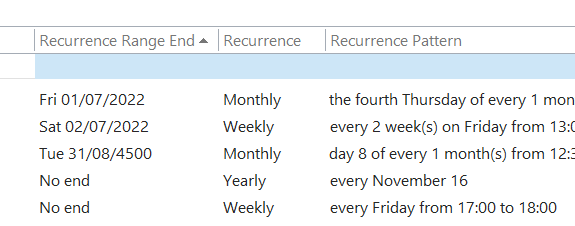
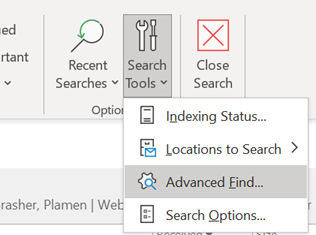
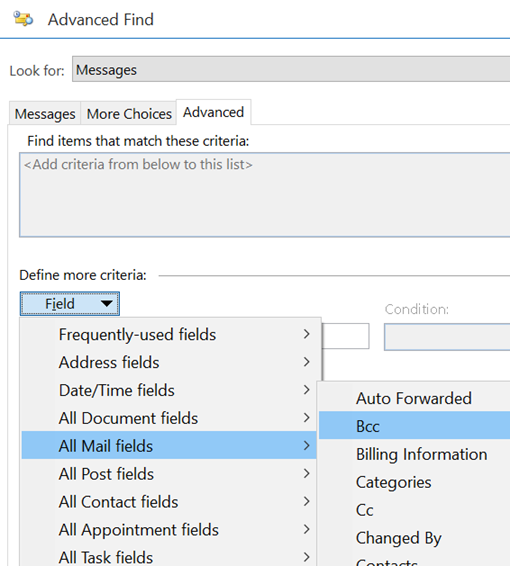
It used to be easy: you had an inbox (real or electronic) and new mail arrived. You’d check the inbox for anything that needed your attention, otherwise just get on with whatever it is that you were doing otherwise. Now, there are so many messaging apps that it can be a headache to not only keep on top of all the inbound contact, but to recall in which app you were having a conversation you want to go back to.
It might be easy if your professional comms is all done via email, but if you’re an itinerant consultant working with several companies, you might even have numerous professional email addresses too so keeping an eye on them all can be a chore.
There’s always a chance you’ll be dealing with LinkedIn or SMS messages with work connections as well, and with friends and colleagues there might be Facebook, WhatsApp and many more.
Two quick tips this week might help to get on top of things, if only a little.
Finding work-related messages in M365
If you use Teams and Outlook for work, with Microsoft 365, then you might already experience discombobulation when looking for something a colleague sent, or some comment discussed in the context of a project… was it in the status email, or in the chat of a meeting? Or a direct message in Teams?
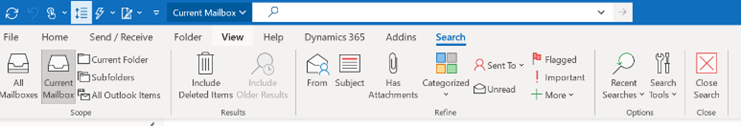
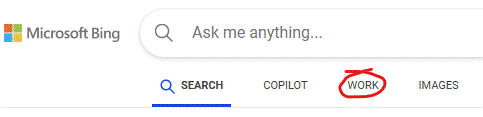
Fortunately, the “Work” search options might be able to help. If your organization has it enabled, go to either Bing.com/work or look at the search option in Office.com while you’re signed in, and you’ll be able to search documents and other sources of data within your M365 environment.
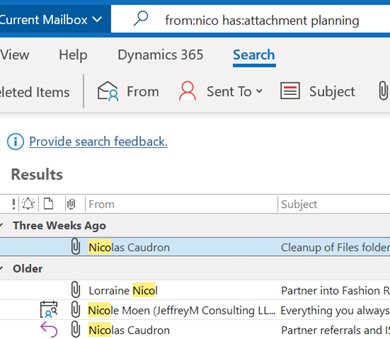
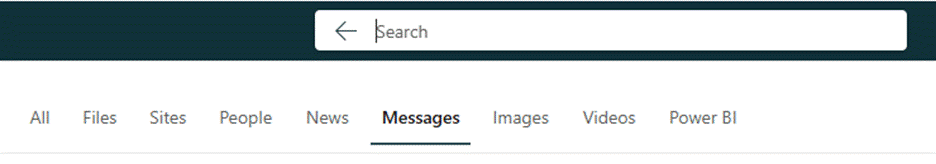
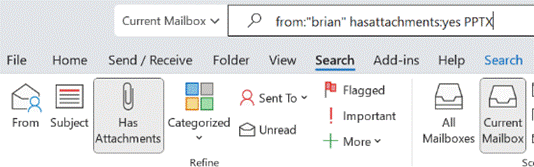
One such is Messages – and the handy shortcut to jump there is aka.ms/messages. Type a search term in there and it will look across both your Outlook mailbox, but also in any Teams messages you might have been part of. Once you get used to checking it – and using the Work search for documents and other stuff – it’s a game changer.
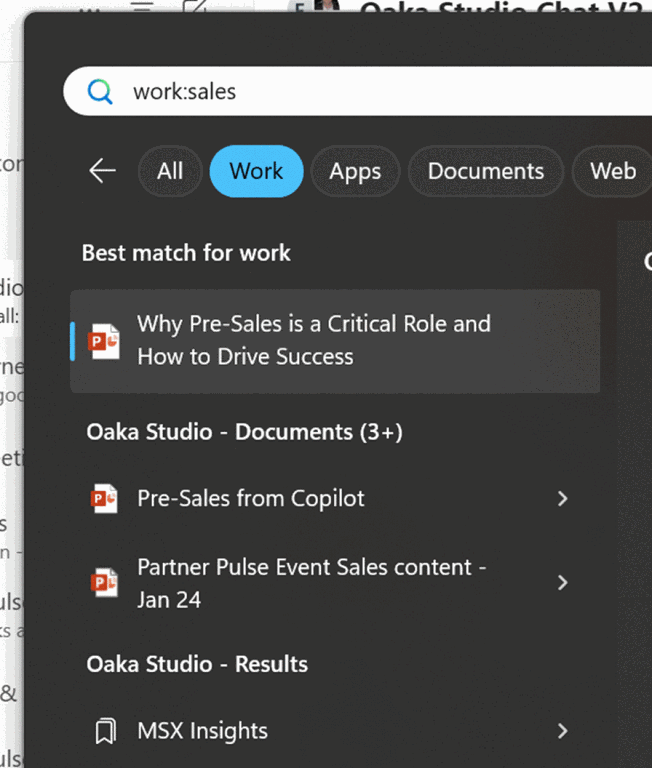
Another trick, for finding documents in your work context, is to search from Windows Search directly by pressing the WindowsKey and typing work: followed by something you’re looking for.
Search across OneNote
Though it’s not strictly messaging, you might have taken notes during a meeting (or even had your friendly Copilot overlord do it for you), potentially spread across several OneNote notebooks.
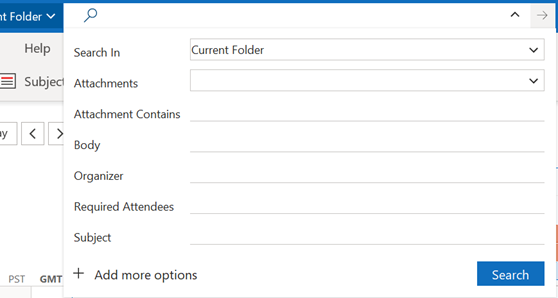
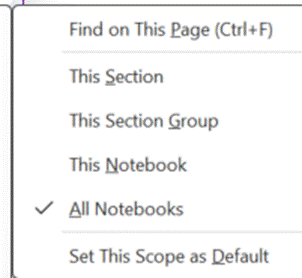
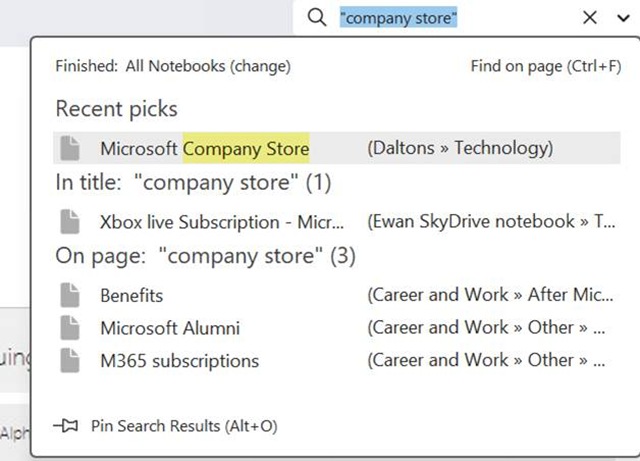
The search box in OneNote lets you choose if you want to perform a query across the current page, section, notebook etc – but the results you get back can be a bit clumsy to interpret as it doesn’t give any details on which are really old pages and which might have been written recently.
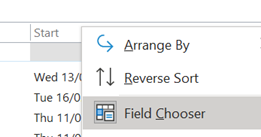
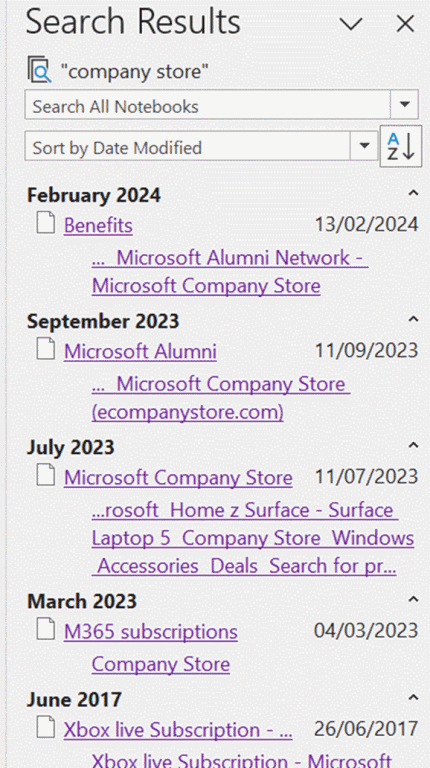
If you haven’t discovered the obscure ALT+O to pin search results, try it out – it lets you group by section, page title or date, and you can expand and collapse the groupings to help locate the most likely page more quickly.







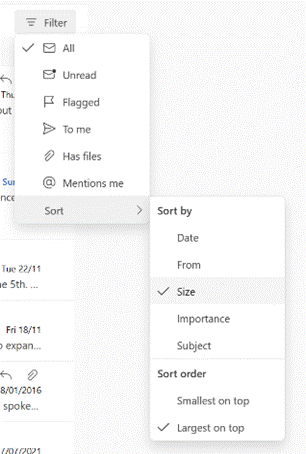
![clip_image002[6] clip_image002[6]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/clip_image0026_thumb.png)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/clip_image0044_thumb.jpg)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/clip_image0064_thumb.png)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/clip_image0084_thumb.png)

![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0024_thumb.gif)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0044_thumb.gif)
![clip_image006[4] clip_image006[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0064_thumb.gif)
![clip_image008[4] clip_image008[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0084_thumb.gif)
![clip_image010[4] clip_image010[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0104_thumb.gif)
![clip_image012[4] clip_image012[4]](/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/clip_image0124_thumb.gif)