Looking back over the last 50 years of technology progress, the internet must surely be the most significant change enabler. When the developing ARPANet adopted TCP/IP in January 1983, the ‘net as we know it started to really take shape. TimBL wrote up an idea of how to connect pages of info together, and within a few years the Worldwide Web started on one of Mr Jobs’ NeXT machines.
As the web evolved to become more consumer-centric and people got PCs in their home which could connect, life started to shift online, especially when broadband replaced dial-up in the early 2000s. Laptops and WiFi helped to unshackle people from their desks and enabled working and playing from nearly anywhere. Coffee shop owners of the world rejoiced; up to a point.
But the most significant trend has surely been mobile connectivity – initially providing access to the same stuff just on a smaller screen. Now, we’re beginning to see the web and info on it become desktop-free zones. The decline in relevance of the desktop or laptop computer has been coming a long time, as smartphone usage around the world exploded. In the future, we’ll potentially be forced to use phones where a better user experience could well be delivered on a big screen, as service providers try to reduce costs while trying to provide a secure, easy to use experience.
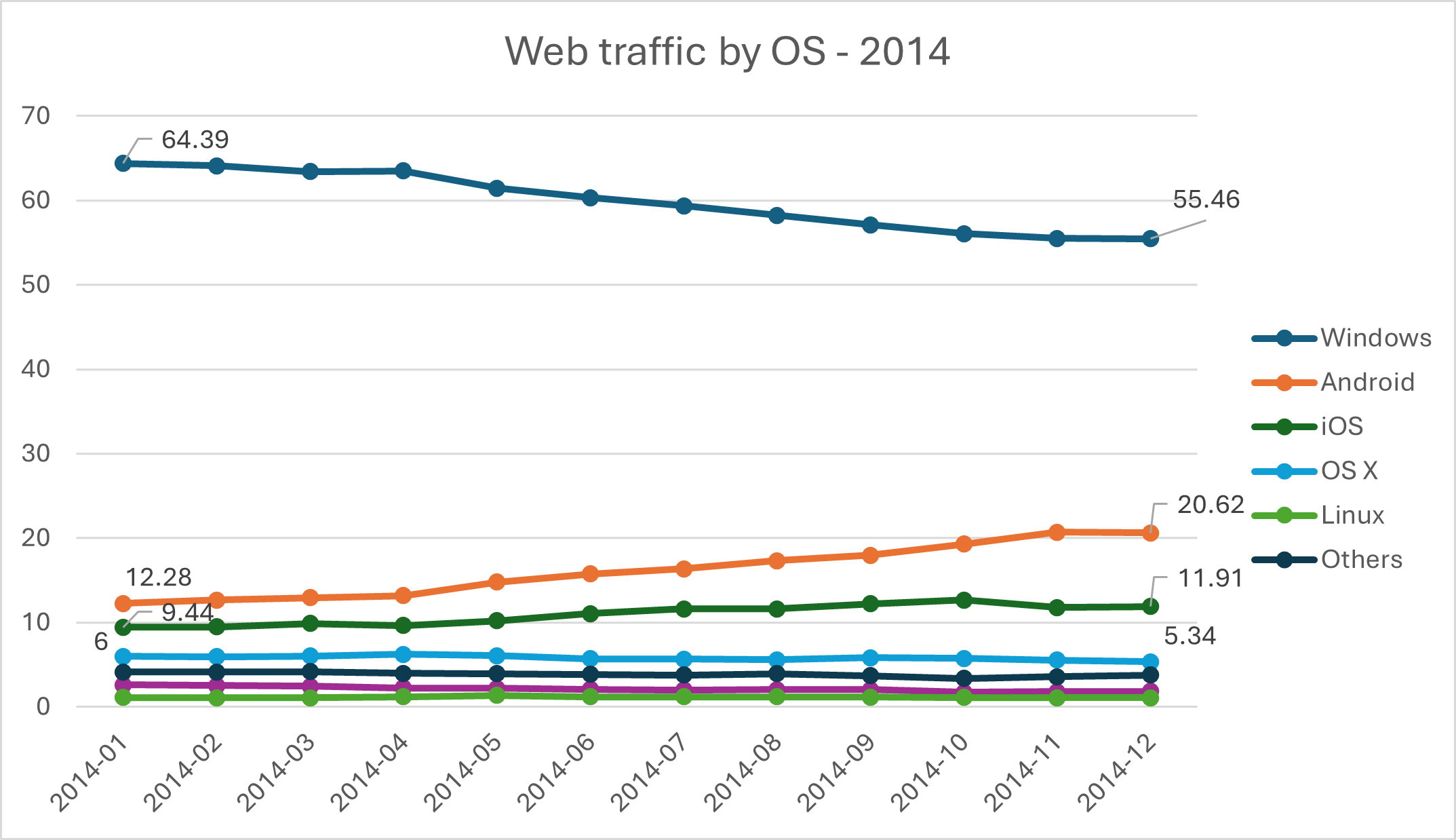
Desktop falling behind
Even in 2014, Windows accounted for nearly 2/3 of web traffic at the start and a bit more than half by the end of the year. Android was taking an early lead over iOS and the Mac had a steady-ish 5%.
Data from statcounter.com
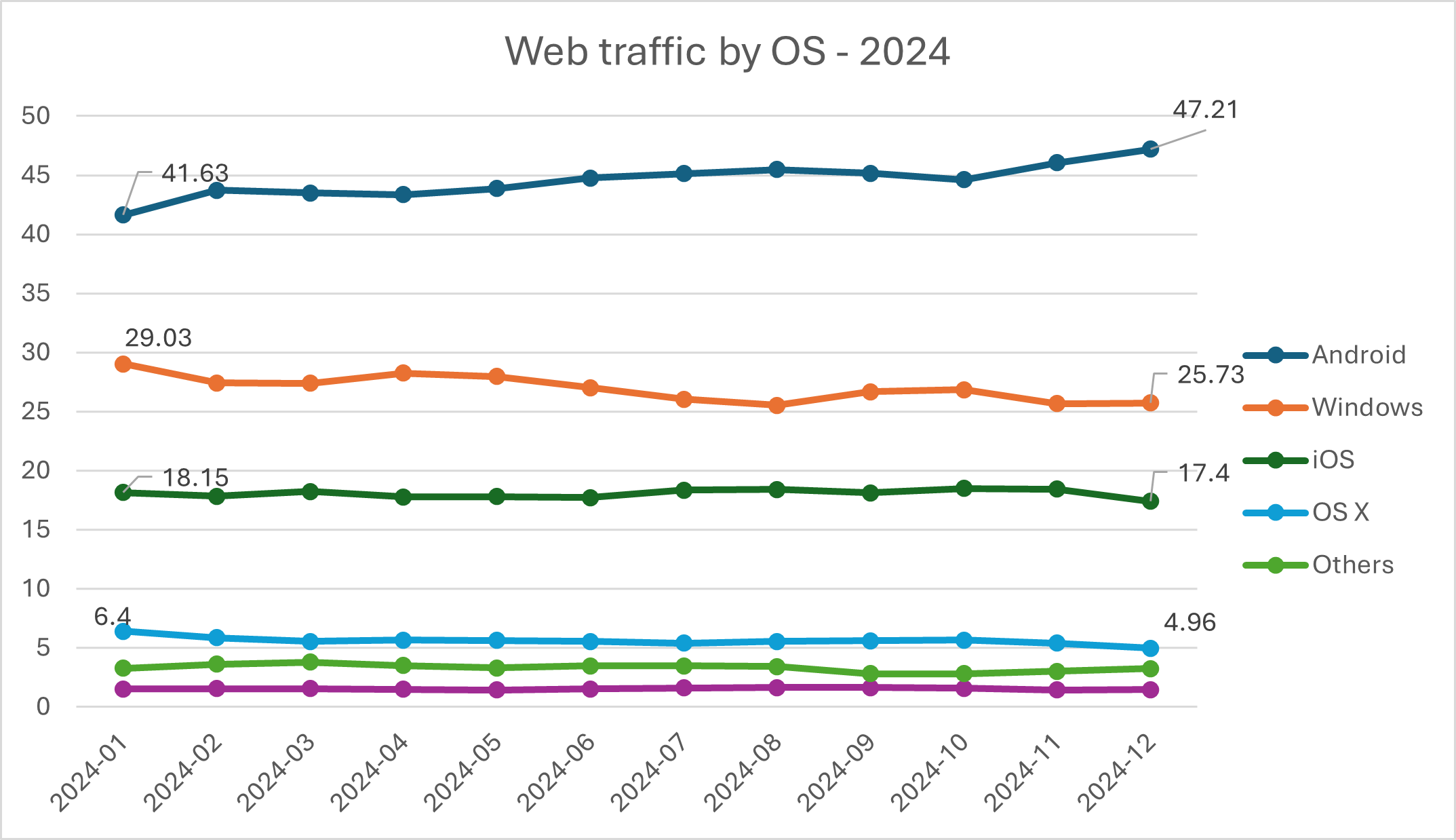
Contrast to the end of 2024 and two-thirds of all traffic is from Android and iOS, with Windows & Mac together just over 30%.
Looking beyond which mobile or desktop OS you use, Chrome is the default browser cross-platform with two-thirds of all traffic, while on the desktop, Microsoft Edge has about 13%. Looking at mobile only, Edge has less half of one percent of usage (beaten slightly by Firefox, and Opera has 4 times the usage) though it’s available for both Android and iOS. You have to wonder when Microsoft will pull the plug, even if the mobile Edge browser is a decent effort (especially so if you use Edge on Windows PC too).
Apps taking over, not always for the better
It’s not just that content is moving to be more mobile-oriented; increasingly, stuff that used to be available on the web can only be done via using an app. To a degree, this could be part of an ongoing enshittification process – a topic we’ll delve into in a future ToW.
As an example, Google has removed the “Timeline” feature from Google Maps online. Discussed briefly in ToW #638, this was a great way of checking where and when you were – handy for doing stuff like mileage claims or remembering how long it’s been since you’ve visited someone.
This particular change has some solid reasoning behind it; rather than The Chocolate Factory storing data about where you’ve been on its servers, they announced that the data would be held securely on the device instead. Is this Google being altruistic and privacy-sensitive, or just trying to avoid being held to account for something down the line? … You decide.
From an end-user perspective, losing access to Timeline in the browser is a bit annoying and too bad if you want to share your history across multiple devices – the data is local to one device only and that’s that. Just in case your phone gets lost, you might want to back it up now…
Un Appy with Online Banking
There are many other examples of websites trying to push you to use their apps (click a link on a mobile browser and it often will try to redirect you), but the biscuit is surely taken by at least one UK credit card provider.
Early digital banking services might have required special hardware or bespoke PC applications, but gradually all went into the browser, with some requiring a hardware token or other device to be used when signing in. Now, it’s very common to need some form of Multi-factor authentication like receiving a one-time SMS message to be able to login; even making a one-off purchase generally requires Strong Customer Authentication.
Users of Virgin Money credit cards have no web-based view of their account, with the options being to use the app or do everything another way. Viewing and download statements can only be done on the phone; the only alternative is to request a paper version be posted.
The in-app help used to advise that if you wanted your statements on a proper computer, then download the PDFs to your phone and email them to yourself. Fortunately, that advice has since been removed…
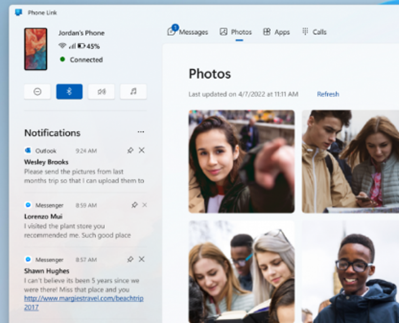
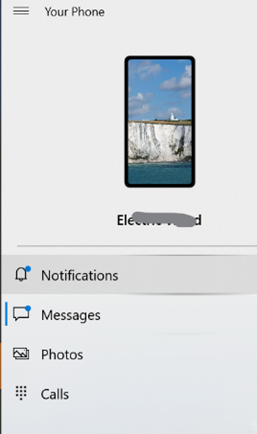
Happily, if you’re an Android & PC user at least, you could use the Phone Link app to browse the file system on the device when it’s connected. The phone will appear in the left pane on Windows Explorer…
… and if you navigate to Phone Name > storage > Download, you’ll be able to view, copy elsewhere on your PC, and even delete the file from the phone storage.
If you’re using OneDrive (the consumer version) for your personal files, you might want to enable the Personal Vault and put potentially sensitive stuff in there.