|
As PC systems evolved over time, and Windows got reliable to the extent that you don’t need to reboot every day or even every week (Windows 7, realistically), the needs of power management also changed as the shift from mains-powered desktop to Lithium-Ion battery laptops gathered pace. Sleep states defined what goes on under the covers in as a PC goes into a different power mode – whether that’s automatic (because of timing, or because the battery level gets to a particular point) or if the user chooses to sleep/hibernate, hits the power button, closes the laptop lid etc. Most PCs could go into a low-power (S3) standby state, where the CPU was shut down but the contents of memory were preserved (still consuming power, but a lot less of it), so the machine can be woken up quickly and carry on as before. After some period in standby or at a point where the battery was about to run out, the PC might even wake up and dump the memory contents to a file on disk, then shut down completely (called hibernating), meaning a subsequent wake-up would take a few seconds longer as it would need to resume from hibernate, since the contents of that huge memory file will be read back in before continuing. Windows 8 introduced the idea of “Connected Standby”, meaning that even when a machine was in a low-power state – to all intents, asleep, but with the CPU still able to run in a restricted manner – the system can maintain a wireless connection that means apps could remain up to date. This was a feature that only applied to modern/Store apps, allowing for synchronising contents in the background while the PC was asleep, so that when it wakes up, the app data and live tiles on the Start screen would be up to date. As both hardware and software platforms have improved, the connected standby idea morphed into Windows 10’s “modern standby”. ToW 335 talked about managing battery states in Windows 10, and briefly discussed using a powerful tool to tweak the way your PC handles standby states. Powercfg is a command line tool, run from an elevated command prompt (ie To check and see what power modes your PC can handle, try running powercfg /a; a more traditional, ACPI desktop will You can get some detailed reporting on how your PC is behaving, by using powercfg with one of the following command line arguments: /energy, /batteryreport, /sleepstudy, /srumutil, /systemsleepdiagnostics or /systempowerreport. SKYPE FOR SIGN OUT, OUTLOOK FOR DISCONNECT Now, one side-effect of this S0 low power mode is that Windows 10 PCs will likely enter that mode shortly after the screen is locked (via timeout or by WindowsKey+L). Non-modern apps (ie Win32/x64 apps like Outlook, Skype for Business etc) won’t know how to deal with this effectively disconnected state, and will drop their connection. This means that when you unlock a plugged-in laptop after being away for a while, you’ll see that Skype for Business is signed out, and Outlook might tell you it’s lost the connection to the server (and then immediately re-connects). If you find this annoying and would rather lengthen the time that elapses when your machine is plugged in, before it goes to connected standby mode, then powercfg to the rescue! From an elevated command prompt, run:
Using the flag /setdcvalueindex instead will tweak the behaviour when on battery only. The value in the first command is the number of seconds before the screen will timeout when locked, so substitute 3600 seconds (ie 60 minutes) for a value of your choice. For further details of what Powercfg can do, see here. |
Tag: Windows 10
Tip o’ the Week 431 – Hiding your name
|
Paranoid Microsoftie Andrew Brook-Holmes went digging to see how to stop this behaviour, and thus inspired this tip. To switch off the display of your name on the login In the right-hand pane, you’ll see a long list of policy items, many of which won’t be configured but could conceivably be; there are options to hide or show elements on the login screen, but in this case we’re going to try not showing the last named user at all. Double-clock on the Interactive logon: Don’t display last signed-in, and you’ll have a simple Enable/Disable choice – in this case, we want to use a double negative – enable the fact that we’re not displaying. If you’d like a more detailed explanation of what it does, there’s another tab on the dialog showing exactly that. Now if you lock your screen (WindowsKey+L), you’ll see t If you use Windows Hello to sign in with your face, then you won’t need to do anything except present your boat race to the camera. If you decide you’d rather go back to normal for easier sign-in, just reverse the process you’ve done above.
Press WindowsKey+R – enter regedit – navigate to… HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System …and set the value of dontdisplaylastusername to 1. Log out to apply the change. |
Tip o’ the Week 429 – Windows 10 April 2018 Update
|
Windows watchers have been talking about this April update for months, as there are many notable updates within, some covered only recently in ToW (425 and 428). As well as Timeline, the Nearby Sharing
You can also right-click on files in Windows Explorer to Share them the same way, and it’s likely to appear in the Share experience of other apps too. The next-to-useless Windows 10 option previously known as Quiet Hours (as per ToW 414), has been given a revamp and a rename, now known as Focus Assist. The intent is not only to silence your machine at times when you don’t need to know stuff (who’s ever been woken at 6am to be reminded that it’s some random LinkedIn person’s birthday, or that there’s an all-day event in your calendar?), but also to control the blizzard of “toast” notifications that modern apps may otherwise throw at you. Note – traditional apps, like Outlook, can still throw up notifications, but if your machine is in a Focus assist mode For a full breakdown of everything else that’s new in the April update, see here. |
Tip o’ the Week 419 – What’s the time?
|
Windows 10 tweaked the way time is In the Windows Insiders builds of the last few weeks – currently 17101 (which is now in the Fast Ring), there have been changes that bring the clock further forward too – the Game Bar has been updated to include the clock on the What is time? Existentially, time is relative. If you ever find that your Windows PC isn’t keeping time accurately, you may want to check that you have it set to get its time automatically (check Settings -> Time & Language – > Date & time), or go into the old-fashioned Control Panel, search for time and look at the settings in there, especially under the “Internet Time” tab to see where it’s syncing the time from: time.windows.com is probably the default. Windows Time is also a thing – the number of milliseconds since the machine was started up, and also the name of the Back to simple relativity, though – what is the actual, real “time”? If you have multiple clocks, watches, phones & PCs, it’s a fair bet that they’ll all be divergent, unless they’re all being synchronised by some external device (your broadband router, maybe). If you’d like to find out exactly what the time is and don’t have access to an atomic clock or similar, there are a few online resources that might help… and you could even try asking Cortana, as she knows about time zones and stuff. But the best time site is http://time.is. Try it from any device and you’ll get the time right now; some allowances need to be made for network latency but the operators have tried For an illustration of what latency (as ultimately governed by the speed of light) means when accessing nearby vs far away websites, check out www.azurespeed.com, which measures the time to connect to storage services at Azure datacenters. Some variance could be explained by performance spikes and so on, but the main impact is network latency due to distance travelled. The results can sometimes be surprising. |
Tip o’ the Week 418 – Preview Apps on Windows 10
|
Way down in the text of the latest announcement, there’s mention of a new “App Preview” program which lets the quick & the brave get access to cool but maybe unfinished updates to Apps they like, but maybe aren’t as dependent on, as the stability of the whole operating system. The first wave of apps that are Preview-enabled, will let more cautious Insiders experience the latest versions of …
There are regular updates to the core apps for every Windows user, not running an Insider build. If you’d like to check, just go into the Store, activate the “…” ellipsis on the top right, and choose Downloads and updates, and review the list to see what apps have been updated and when, or hit “Get updates” to check for published updates to other apps. The Photos app has a new opt-in feature, in conjunction with a test app that is designed to make it easy to share Photos from a phone to a PC; even if you’re not running an Insider build, you can turn on the mobile import… The “Photos Companion” test app makes a point-to-point connection between phone & PC (ie they need to both be on the same network), and by going to the Import menu within the PC Photo app, a QR code will be displayed on-screen.
Of course, you could use OneDrive on your mobile device to automatically sync photos to a Camera Roll folder in your cloud storage location; it has a bit of latency, usually, so you might find it takes a few minutes before the photo you’ve just taken has uploaded and is ready to be accessed or shared. The Import over WiFi feature is handy to share right away, or to share with PCs that aren’t set up with your OneDrive, such as a friend’s PC, or if you’re working on a project where you want to collect photos from a group of people in a short space of time – maybe doing a collaborative video or something similar? |
Tip o’ the Week 414 – So Quiet…. Shhhh! Shhhh!
|
“Redstone” is the internal Microsoft codename for the current branch of Windows 10 If you’re at all confused by the nomenclature – the names of the updates rather than the codenames – then you’re not alone. Redstone 4 is currently in development, is being pushed out to Windows Insiders and will arrive within a few months to everyone else, if all goes to plan. Petrolheads / Gearheads may be glad to know that an RS4 will be arriving soon, even in the USA – even if it’s a software update for Windows.
ToW #343 covered how to replicate Quiet Hours – where you could set your PC to not blare stupid reminders in the middle of the night, should it still be switched on – but in RS4 this won’t be necessary as you’ll be able to choose when, and where, Quiet Hours will be enabled. Once you know you have a RS4 build of Windows with the Quiet Hours feature – 17074 or later – then just got into Settings, and search for Quiet. Now, shhhhh. |
Tip o’ the Week 413 – Got Skills, they’re multiplying
|
The personal assistant market (somewhat incorrectly referred to as “AI”s by the mass media) is being talked up as a new frontier, of voice control meeting smart language understanding and connectivity. Apple were first to the market in the public consciousness with Siri, but now that Amazon’s Echo and Google’s Home devices have been very sucessful (the Echo Dot being Amazon’s top selling bit of kit over the holiday season), the idea that people would use a phone as the main way to voice-interact with online services seems a little less assured than it was a couple of years back. Alexa has led the way with integrating Amazon’s device and service, with other devices and services – just as the app made the smartphone useful and pervasive, the “skill” support of your chosen digital assistant seems set to make or break that ecosystem. Amazon has talked up having over 25,000 skills for Alexa – really impressive, though like smartphone appstores, there are a lot of “fart app” equivalents in there, amongst the good stuff.
The Cortana skills kit promises to make it really easy for developers to add Cortana support for their apps and services, though Cortana Skills are still officially “in preview”. Alexa and Cortana may yet get friendly – though it hasn’t happened quite in the timescale envisaged. Despite reports, Cortana is not dead, yet – there are device partnerships being announced and due to be announced. And the Cortana assistant is available on Android and iOS; Samsung S8 users could even remap the Bixby button with Cortana, though unofficially. If you’ve a PC with the latest OS, you can get Cortana by pressing WindowsKey+Q, or even WindowsKey+C (to go straight to Cortana’s voice input), or even by saying “Hey Cortana” (check in Settings, look for Cortana). If you’re in the US, then you may be able to access Cortana Skills straightaway – there’s no installation or association required (like you’d need to do with Alexa skills), though you might need to configure or authorize the skill on first run. Check out the list of supported Skills, here – there are quite a few fillers (yet more guff apps) making up the modest 250-odd skills available, but there are some good ones there too – see the featured skills for example.
For previous coverage of Cortana on ToW, see #380, et al. |
Tip o’ the Week 409 – Touchpad settings
|
Microsoft has had a few funny KB articles over the years, too, though not necessarily intended to amuse. Barney sometimes plays on his own…, for example – who knew?
Given that a defining feature of mechanical meeces was the fact they had a rubbery ball inside, it seemed obvious to early laptop designers that a trackball would make sense to move the pointer around. Eventually the touchpad took over, and divided opinion – some people just couldn’t live without a USB-tethered proper mouse, which they carted around with their laptop, while designers sought to add more and more functionality to the touchpad.
On a Windows 10 laptop, if you type touchpad at the start screen to find the settings that control it, you’ll see a load of If you’re especially particular about how your touchpad works, you may wish to look into tuning it further through registry tweaks. |
Tip o’ the Week 406 – A path! A path!
 One issue that’s plagued the user experience of computer application design, is the traditional need to force the end user to understand the file system of their machine. In a nutshell, the hierarchy that operating system designers decided was a necessary way of storing or at least referencing files (and it is generally a Good Thing) can be a bit confusing for users who don’t need to know how the internals of their OS work. They might tinker with the contents of the C:\Windows folder too, thinking that it takes up rather a lot of space… Fortunately, Windows now provides a few layers of protection to stop users from knackering their own machines, so that’s less of a problem now. One issue that’s plagued the user experience of computer application design, is the traditional need to force the end user to understand the file system of their machine. In a nutshell, the hierarchy that operating system designers decided was a necessary way of storing or at least referencing files (and it is generally a Good Thing) can be a bit confusing for users who don’t need to know how the internals of their OS work. They might tinker with the contents of the C:\Windows folder too, thinking that it takes up rather a lot of space… Fortunately, Windows now provides a few layers of protection to stop users from knackering their own machines, so that’s less of a problem now.
Allowing users to save stuff to their local hard disk was also often a good way of helping them lose data, as there probably won’t be a backup of the most important files that the user has stuffed somewhere in their own twisted hierarchy of files & folders. There are numerous ways for users to be blocked from saving stuff to their own PC, forcing them instead to put data onto some networked share. App designers – especially “modern” apps in Windows, or mobile apps meant for other platforms like iPad or Android – may present a simplified UI to guide users to put stuff in commonly referenced folders by default, and hide access to any off-piste areas too. Fortunately, with file synchronisation systems like OneDrive When dealing with any files that are also synched somewhere, it’s often handy to get the path that either points to the location of the file (to save you clicking through the hierarchy to arrive at it), or indeed directly to the file itself…
Still the most useful hidden command, some say, is the Copy as path option. Right-click a file in Windows Explorer, and you’ll see a bunch of context-sensitive stuff you can do.
|
Tip o’ the Week 399 – What’s in Store?
|
The original idea behind the Apps that were to be distributed via the Store was that they would be easy to install and share, but perhaps most importantly, heavily sandboxed so they couldn’t hog the performance of the machine, couldn’t be a vector for attack by spreading malware and the likes or drain the battery of the laptop (or phone) through excessive background execution. Anyone who’s ever looked in Task Manager on their PC and seen Runtime Broker run amok might disagree that it’s worked out, but ‘tis still a noble aim. The idea of Windows Store apps evolved into Universal Windows Platform apps in Windows 10, the plan being that the same app could run on PCs, Hololens, Surface Hub, phones, Xbox…
There’s nothing obviously new in the Store app yet, but MJF reports that Progressive Web Apps will be featured in the catalogue of apps in future. In other news, the bricks’n’mortar Microsoft Store is coming to London. |





































 , it’s very easy to both write data to the local machine and also to sync it with the cloud, more-or-less immediately. These solutions mean you put stuff on your own PC’s file system, but nothing you write to it will be orphaned there – so if you move to another PC, or your machine gets wiped or lost, you’ve still got access to everything.
, it’s very easy to both write data to the local machine and also to sync it with the cloud, more-or-less immediately. These solutions mean you put stuff on your own PC’s file system, but nothing you write to it will be orphaned there – so if you move to another PC, or your machine gets wiped or lost, you’ve still got access to everything.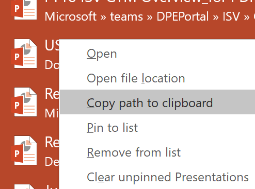 Right-clicking within the most-recently-used files list from the File menu in Office apps often gives you the chance to open the location of the file or copy
Right-clicking within the most-recently-used files list from the File menu in Office apps often gives you the chance to open the location of the file or copy  its path to the clipboard, for later consumption, like pasting a link into email (though with the Attach File option in Outlook now offering a most recently-used files list, it may be unnecessary to grub around looking for where the file is – just click the list to add it).
its path to the clipboard, for later consumption, like pasting a link into email (though with the Attach File option in Outlook now offering a most recently-used files list, it may be unnecessary to grub around looking for where the file is – just click the list to add it).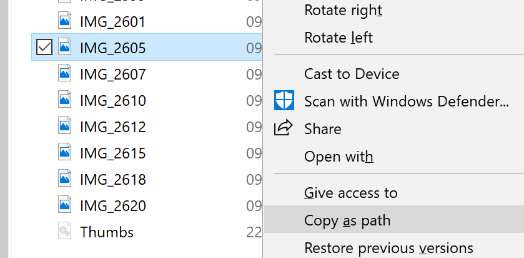 Hold SHIFT while you right-click the file, and you’ll get an extra option to copy its path (in fact, the full filename including its path) to the clipboard, for future use. Once you remember this neat shortcut, you’ll use it far more often than you’d think – especially if you deal with inserting images into web pages, emails etc.
Hold SHIFT while you right-click the file, and you’ll get an extra option to copy its path (in fact, the full filename including its path) to the clipboard, for future use. Once you remember this neat shortcut, you’ll use it far more often than you’d think – especially if you deal with inserting images into web pages, emails etc.
