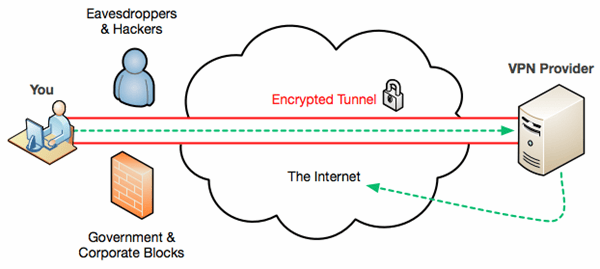
Before widespread internet access, companies would use modems and dial-up services so remote workers could access their internal network as normal, but connecting (slowly) over a phone line. As mobility and broadband became more pervasive, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provided a way of accessing data that is held within your place of work – or home, perhaps – when you’re out on the road, establishing an end-to-end secure link over the internet between you and the destination.
At the same time, many of the services we’d rely on moved fully online – like email, shared documents or even business applications, potentially hosted by a 3rd party like Salesforce, Dropbox, Workday or Microsoft. Each of those would be protected using an encrypted and authenticated SSL/TLS connection, just like any other secure website connection.
What do you still have in your home or in your business premises, which you’d need a VPN to access? For organisations with local services or apps, Microsoft has long championed an automatic VPN back to your company HQ, called DirectAccess, but that is now having the sun set on it in favour of a more modern Always On VPN. Many businesses now are all in the cloud, so have nothing internally to connect to – but even as a home user, there may be some relevance.
Securing the connection
When you link using a VPN, everything between you and the endpoint is encrypted through an established “tunnel”, and therefore invisible to the intervening points on the network.
The invisibility of what’s happening in the tunnel could be useful to the user, for example where there’s a policy denying access to certain websites; if you VPN (and that was allowed) then the network owner wouldn’t know what you were sending up and down the connection since it’s encrypted, and therefore might not be able to block your access.
The VPN model illustrated above has all your internet traffic going back to the VPN endpoint and then out onto the internet from there (so it looks to the website you’re accessing like you’re located wherever the VPN endpoint is). There’s generally a performance penalty in doing this since there are additional “hops” involved, and it also means that whatever you’re getting up to on the public internet will be happening through your company’s firewall or your own home router.
Some VPNs give you the option to split traffic, where it routes only certain data down the VPN tunnel, while everything else just goes out onto the internet from the hotel/airport etc network as usual. That reduces the load on the VPN endpoint and its network (since casual browsing traffic isn’t coming in and out, only stuff destined for the internal network it is attached to), and is a bit quicker for the user since they just get their public internet stuff done nearby.
Some companies – mostly VPN vendors or security consultancies, it must be said – would advise that every time you connect your laptop to a public WiFi network (as found in coffee shops, airports, hotels etc), then woe betide you if you don’t access everything through their subscription VPN service. Such services would say you should routinely connect to their endpoint (in whichever country you want) so that everything between you and their server is encrypted, and the local network provider to you has no clue what you’re doing.
NordVPN, probably the market leader for 3rd party services, pushes itself heavily through advertising and tie-ups with leading podcasts and credit card companies, etc.
Securing the connection is one thing, however there’s still the small matter of being tracked in everything you do, potentially having unwanted software downloaded, which a 3rd party VPN might not protect you from, so it’s no silver bullet.
If you don’t use a VPN and you’re accessing a shopping site or online banking, the network provider (eg the Hotel or airport) could see which URL you’re accessing, but since the first thing you’ll do in nearly every browser session is to establish a secure connection between your computer and their website, any prying networking provider would only see that you’re sending gobbledygook data back to a single address out there on the net.
There is a possibility of having a man-in-the-middle attack which steals your data through subterfuge, though there are numerous steps taken to prevent this. If you’re using a VPN then you’re protected, unless you’re unwittingly VPNed into the man in the middle directly, in which case, the whole game’s a bogey.
Pretending to be somewhere you’re not
Some VPN users will use them to appear that they are somewhere else – eg if you’re travelling but want to access a web service which is locked to a given region, like TV streaming services. Lots of Brits in America use VPNs to access the BBC’s iPlayer, for example. There is a “yes, I have a TV license” checkbox, but we all know how effective those kind of prompts are.
Since the traffic from the VPN device or service appears to be from whatever country it’s in, that might be used to circumvent geographic blockers. Streaming companies often have legitimate reasons to restrict access based on where you are (as opposed to just being greedy and horrible).
Since some VPNs are offering ways to not only defeat the geo-blocking, but potentially provide a way around password sharing restrictions, the arms race will continue where content providers will try to stop people using certain services and VPN services will get smarter at not being blocked.
Further reading
If you’re on the road and want to access stuff back in your home, your broadband router might even have a VPN service built in (though do take care that it’s not using out of date security standards). Another option could be to set up an endpoint with OpenVPN. If you have Synology NAS appliance (and they are very good), you can enable the OpenVPN service relatively easily – see here.
Some other things to check out:
· Should You Use a VPN? – Consumer Reports
· Do I Really Need a VPN at Home? | PCMag
· Is a VPN really worth it? | Tom’s Guide (tomsguide.com)
So, back to the original question – do you really need a VPN?